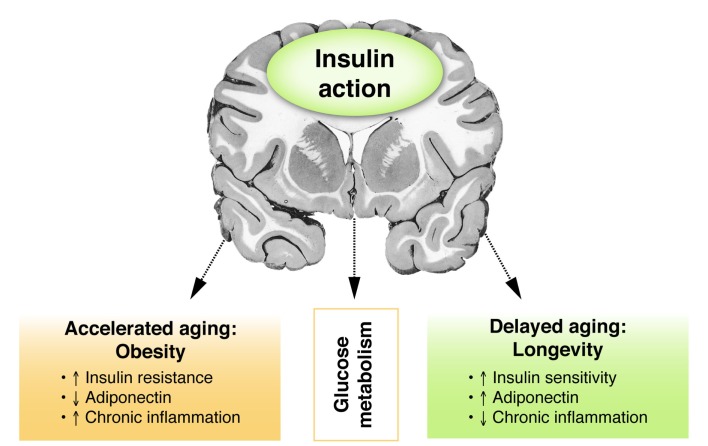
Figure 3.
Insulin and the brain: models of accelerated and delayed aging. Figure showing the putative relationship between central insulin action and glucose metabolism in models of accelerated or delayed aging. Obesity as a model for accelerated aging is associated with peripheral insulin resistance, decreased adiponectin levels, and enhanced chronic inflammation. Opposite features are observed in healthy longevity as a model of delayed aging.