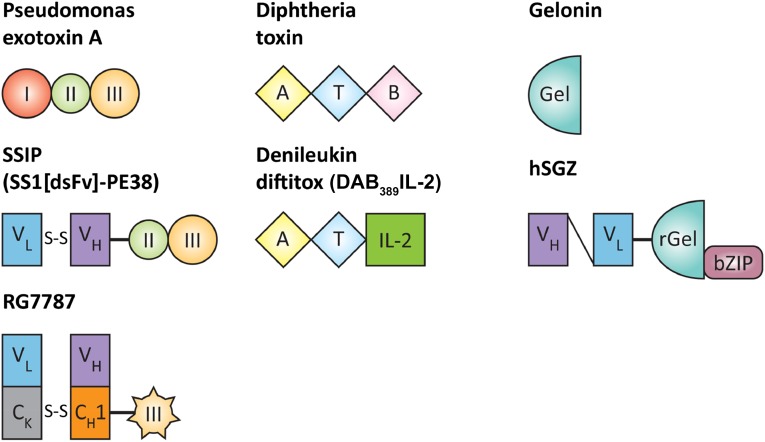
Figure 1.
Structure of select toxins and immunotoxins. Native Pseudomonas exotoxin A contains three domains: domain I (binding), domain II (unknown function), and domain III (catalytic domain). In the SS1P immunotoxin, domain I is replaced by a double-stranded Fv (VL and VH) that targets mesothelin. The engineered disulfide bond links VL and VH. The RG7787 immunotoxin uses a humanized Fab fragment and lacks PE domain II. Diphtheria toxin also contains three domains: catalytic, transmembrane, and binding. In denileukin diftitox, the B domain is replaced by human IL-2 to permit binding to cells bearing the IL-2 receptor. Gelonin is a plant toxin with n-glycosidase activity that inhibits ribosomal activity to halt protein synthesis. It consists of a single domain. In the hSGZ immunotoxin, recombinant gelonin is fused to a single-chain Fv (VL and VH) that binds fibroblast growth factor receptor 14-kDa protein (Fn14), and a bZIP domain that increases activity of the immunotoxin by allowing dimerization.
Abbreviations: A, catalytic domain; B, binding domain; Gel, gelonin; IL-2, interleukin-2; rGel, recombinant gelonin; T, transmembrane domain.