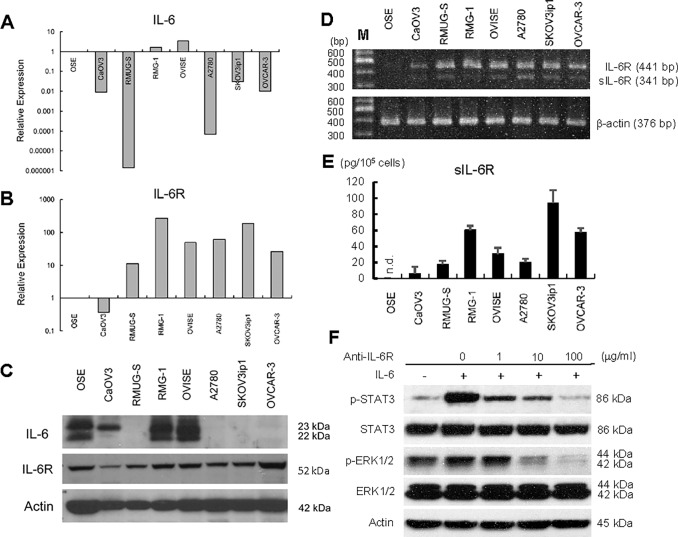
Fig 2. Expression of IL-6 and IL-6R in ovarian cancer cell lines.
Real-time RT-PCR of IL-6 (A) and IL-6R (B). Total RNA was collected from seven different ovarian cancer cell lines using TRIzol and subjected to real-time RT-PCR. The 2-ΔΔCT method was used to calculate the relative abundance with respect to GAPDH expression. Relative fold differences with respect to primary ovarian surface epithelium (OSE) are presented. (C) Western Blot. Cell lysates from seven ovarian cancer cells were resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with an antibody against IL-6 and IL-6R. β-Actin was used as a loading control. (D) RT-PCR. RNA was collected and the expressions of full-length IL-6R (IL-6R) and soluble IL-6R (sIL-6R) expression in ovarian cancer cell lines were examined. PCR conditions were as described in Material and Methods. (E) ELISA assay of sIL-6R. Seven ovarian cancer cells (1 x 105 each) were plated onto 24-well plates and cultured with 1 ml of serum-free medium for 72 h. Conditioned media were collected and the concentration of human sIL-6R was measured by ELISA. Experiments were repeated three times. n.d.; not detected. (F) Western Blot. Exogenous treatment of IL-6 activates IL-6/IL-6R signaling in ovarian cancer cell lines. SKOV3ip1 cells were stimulated with IL-6 (100 ng/mL) for 30 minutes with or without pretreatment using ranti-IL-6R antibody (1–100 μg/ml) non-immune IgG as control. Cell lysates were collected and equal amount of cell lysates (30 μg) was resolved by 10% SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with anti–phosphorylated STAT3 (p-STAT3) antibody and anti–phosphorylated p44/42 MAPK (p-ERK1/2) antibody. The membranes were stripped and rehybridized with antibodies detecting the total forms of the protein. Blots are representative of three experiments.