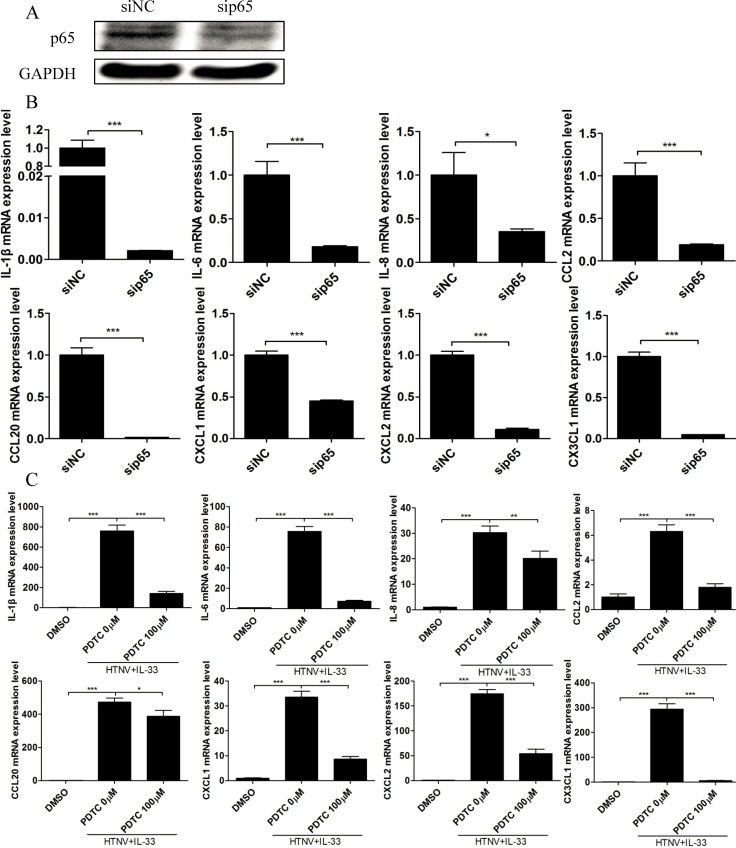
Fig 7. Divergent effects of sip65 and PDTC on IL-33-mediated inflammatory responses in HUVECs infected with HTNV.
(A) An siRNA specific to p65 was transfected into HUVECs for 6 h, and the cells were treated as indicated above. Half of the cell lysate was collected, and the expression of p65 and GAPDH was analysed by western blotting. (B) RNA was extracted from the other half, and the mRNA levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines were determined by real-time PCR. All the experiments were repeated in triplicate. The mRNA data were generated from three independent experiments using three independent HUVECs donors. (C) HUVECs were first exposed to PDTC (100 μM) for 2 h and infected with HTNV (MOI = 1) for 48 h and treated with IL-33 (20 ng/ml) for another 6 h. Cells in a medium containing DMSO were set as the reagent control. RNA was extracted from these cells, and the mRNA levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines were determined by real-time PCR. All the experiments were repeated in triplicate. The mRNA data were generated from three independent experiments using three independent HUVECs donors. Data are the means ±SE. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, siRNA specific to p65 versus siNC-treated cells, PDTC 0 μM versus PDTC 100 μM, or PDTC 0 μM versus the DMSO control.