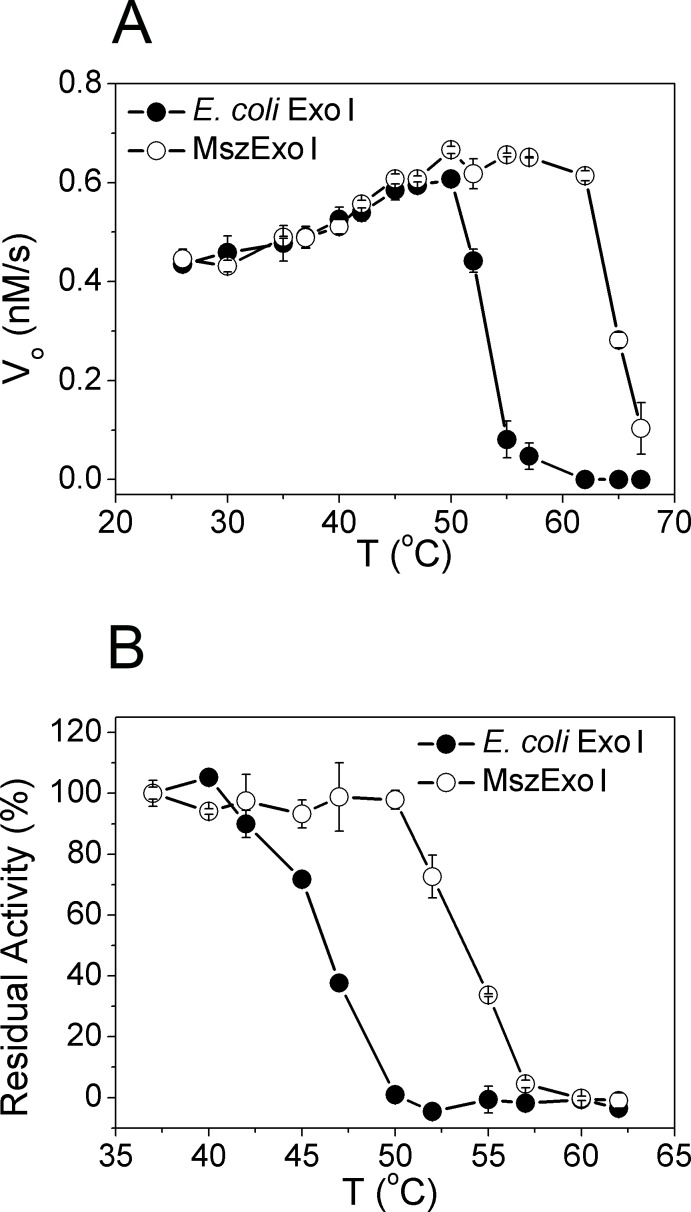
Fig 5. Thermal profiling of E. coli Exo I and MszExo I.
(A) Determining optimum working temperature for two Exo Is. The reaction conditions were 5 nM enzyme, 1 μM ssDNA substrate (half FRET-dT67 with half dT67), 50 mM Glycine-NaOH buffer, pH 9.5, 200 mM NaCl, 0.1 mg/ml BSA and 5mM MgCl2 at given temperature varying from 25 to 67°C. Other details are described in Materials and Methods. MszExo I (open circle) showed broader working temperature than E. coli Exo I (filled circle). Errors were calculated from three parallel experiments. (B) Thermal stability of two Exo Is evaluated by thermal inactivation assay. In this assay, 15 nM enzyme in standard reaction buffer was incubated at given temperature varying from 25 to 62°C for 10 min, then cooled on ice, and finally activity was determined at 37°C. The data were normalized by taking the activity of enzymes incubated at 37°C as 100%. Errors came from three parallel experiments. Thermal stability of MszExo I was by 5°C higher than that of E. coli Exo I.