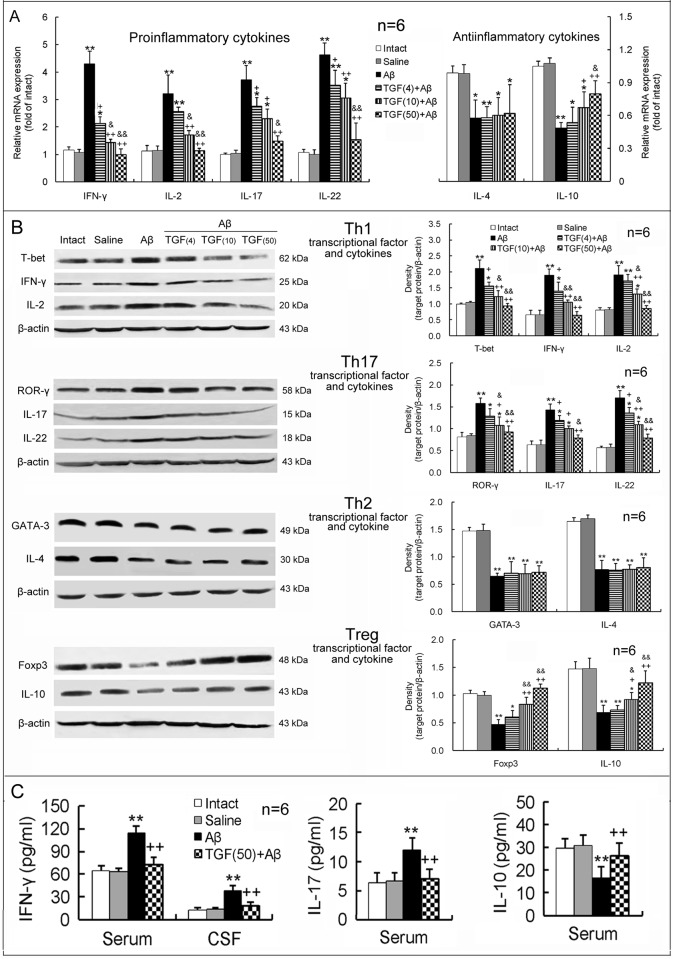
Figure 5. ICV TGF-β1 pretreatment prevents Aβ1–42-induced imbalance in proinflammatory/antiinflammatory responses of T lymphocytes.
TGF-β1 (4, 10 or 50 ng in 5 μl) was given ICV one hour prior to Aβ1–42 injection. On day 7 following TGF-β1 administration, differentiation and function of Th1, Th17, Th2 and Treg cells were assessed by measuring levels of specific transcriptional factors and cytokines in the hippocampus, serum and CSF. (A) Gene expression of T lymphocyte-related proinflammatory and antiinflammatory cytokines in the hippocampus. (B) Protein expression of specific transcriptional factors (T-bet, ROR-γ, GATA-3 and Foxp3) and cytokines of T lymphocyte subsets in the hippocampus. (C) Concentrations of Th1- and Th17-related proinflammatory cytokines (IFN-γ and IL-17) and the Treg-related antiinflammatory cytokine (IL-10) in serum and/or CSF. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, versus intact or saline-treated rats; +p<0.05, ++p<0.01, versus alone Aβ1–42-injected rats; &p<0.05, &&p<0.01, versus 4 or 10 ng of TGF-β1 administered rats. Aβ = Aβ1–42; TGF(4) = 4 ng of TGF-β1; TGF(10) = 10 ng of TGF-β1; TGF(50) = 50 ng of TGF-β1.