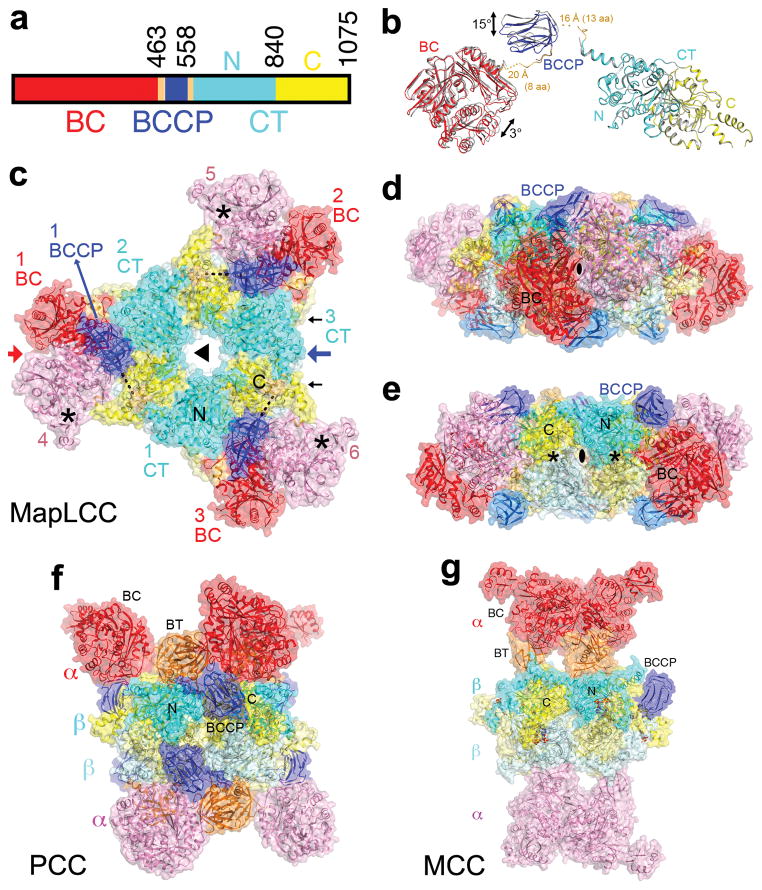
Figure 1.
Crystal structure of M. avium subspecies paratuberculosis long-chain acyl-CoA carboxylase (MapLCC). (a). Domain organization of MapLCC. The domains are labeled and given different colors. (b). Overlay of the structures of the two MapLCC monomers in the asymmetric unit (one in color, the other in gray). Residues (aa) that are missing in the linkers from BCCP are indicated with dashed lines. (c). Overall structure of the 720 kD hexameric holoenzyme of MapLCC. The six monomers are labeled. The domains in the three monomers in the top layer (numbered 1, 2, and 3) are colored as in panel a. The BC, BCCP, N and C CT domains in the three monomers in the bottom layer (numbered 4, 5, 6) are colored pink, pale blue, pale cyan and pale yellow, respectively. The disordered region of the BCCP-CT linker is indicated with the dashed line (black). The BC active sites are indicated with the asterisks (black). The CT active sites are on the side of the CT domain core, indicated with the black arrows. (d). Structure of the MapLCC holoenzyme viewed down the BC domain dimer (red arrow in panel c). (e). Structure of the MapLCC holoenzyme viewed down the blue arrow in panel c. The CT active sites are indicated with the asterisks (black). (f). Structure of the 750 kD α6β6 PCC holoenzyme 10. The view is equivalent to that of panel d. (g). Structure of the 750 kD α6β6 MCC holoenzyme 11. The structure figures were produced with PyMOL (www.pymol.org).