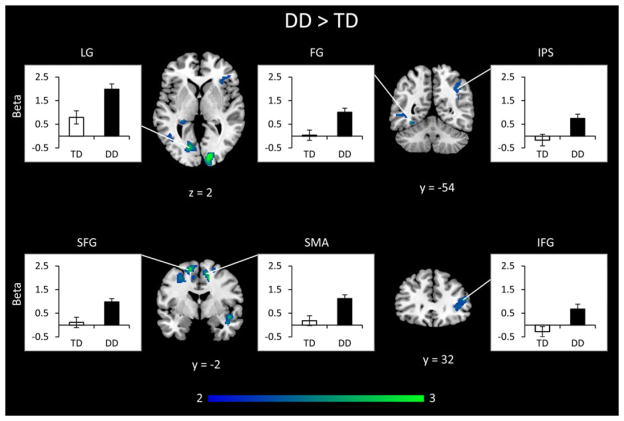
Figure 4. Differences in brain activation between DD and TD groups in combined addition and subtraction data.
Combining data across addition and subtraction problems revealed that children with developmental dyscalculia (DD) had significantly greater activity than typically developing (TD) children in left lingual gyrus (LG), fusiform gyrus (FG), right intraparietal sulcus (IPS), right anterior insula, interior frontal gyrus (IFG), superior frontal gyrus (SFG) bilaterally, and right supplementary motor area (SMA). Threshold as in Table 3, color bar indicates t-score.