Figure 3.
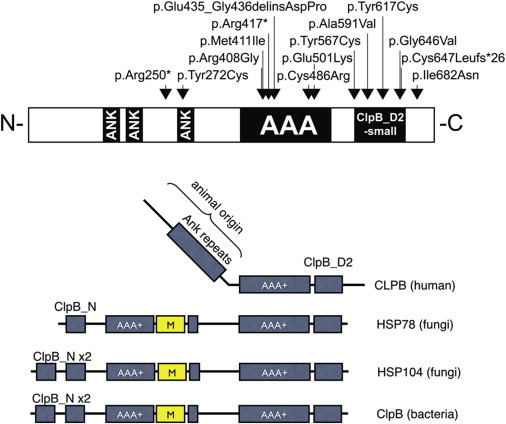
Schematic Representation of CLBP in Human, Fungi, and Bacteria
(A) The positions of all mutations identified in human. Black boxes represent the two main functional domains: the ankyrin domain (ANK) consisting of a short 34 residue repeat implicated in a wide range of protein-protein interactions and the ATPase domain (AAA+).31,32
(B) Evolutionary changes in domain composition of CLPB proteins in human, fungi (mitochondrial HSP78 and cytosolic HSP104), and bacteria. All CLPB-family homologs possess at least a single AAA+ domain and the specific CLPB-D2 domain. In contrast to human CLPB, fungi and bacteria possess an “M domain,” a ClpB N domain, and an additional AAA+ domain. Ankyrin repeats are present only in the human homolog and are probably species specific.
