Table 1.
Definitions of performance measures reported in the studies
| Measure | # | Definition | Formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recall (sensitivity) | 22 | Proportion of correctly identified positives amongst all real positives |

|
| Precision | 18 | Proportion of correctly identified positives amongst all positives. |

|
| F measure | 10 | Combines precision and recall. Values of β < 1.0 indicate precision is more important than recall, whilst values of β > 1.0 indicate recall is more important than precision |
 Where β is a value that specifies the relative importance of recall and precision. Where β is a value that specifies the relative importance of recall and precision. |
| ROC (AUC) | 10 | Area under the curve traced out by graphing the true positive rate against the false positive rate. 1.0 is a perfect score and 0.50 is equivalent to a random ordering | |
| Accuracy | 8 | Proportion of agreements to total number of documents. |

|
| Work saved over sampling | 8 | The percentage of papers that the reviewers do not have to read because they have been screened out by the classifier |

|
| Time | 7 | Time taken to screen (usually in minutes) | |
| Burden | 4 | The fraction of the total number of items that a human must screen (active learning) |

|
| Yield | 3 | The fraction of items that are identified by a given screening approach (active learning) |
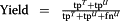
|
| Utility | 5 | Relative measure of burden and yield that takes into account reviewer preferences for weighting these two concepts (active learning) |
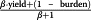 Where β is the user-defined weight Where β is the user-defined weight |
| Baseline inclusion rate | 2 | The proportion of includes in a random sample of items before prioritisation or classification takes place. The number to be screened is determined using a power calculation |
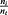 Where n
i = number of items included in the random sample; n
t = total number of items in the random sample Where n
i = number of items included in the random sample; n
t = total number of items in the random sample |
| Performance (efficiency) a | 2 | Number of relevant items selected divided by the time spent screening, where relevant items were those marked as included by two or more people |

|
| Specificity | 2 | The proportion of correctly identified negatives (excludes) out of the total number of negatives |
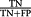
|
| True positives | 2 | The number of correctly identified positives (includes) | TP |
| False negatives | 1 | The number of incorrectly identified negatives (excludes) | FN |
| Coverage | 1 | The ratio of positives in the data pool that are annotated during active learning |
 Where L refers to labelled items and U refers to unlabelled items Where L refers to labelled items and U refers to unlabelled items |
| Unit cost | 1 | Expected time to label an item multiplied by the unit cost of the labeler (salary per unit of time), as calculated from their (known or estimated) salary | timeexpected × costunit |
| Classification error | 1 | Proportion of disagreements to total number of documents | 100 % − accuracy % |
| Error | 1 | Total number of falsely classified items divided by the total number of items |
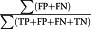
|
| Absolute screening reduction | 1 | Number of items excluded by the classifier that do not need to be manually screened | TN + FN |
| Prioritised inclusion rate | 1 | The proportion of includes out of the total number screened, after prioritisation or classification takes place |
 Where nip = number of items included in prioritised sample; ntp = total number of items in the prioritised sample Where nip = number of items included in prioritised sample; ntp = total number of items in the prioritised sample |
TP = true positives, TN = true negatives, FP = false positives, FN = false negatives.
aPerformance is the term used by Felizardo [13], whilst efficiency was used by Malheiros [14].
[Not used in the included studies, though worthy of note is the ‘G-mean’. This is the geometric mean of sensitivity and specificity, and it is often used for a metric alternative to F score in evaluating classification on imbalanced datasets. G-mean evaluates the classification performance for classification labels, whilst AUC evaluates the classification performance for classification scores. Note that these metrics alone do not always reflect the goal in systematic reviews [15].
