Figure 2. Maximum hand aperture and corresponding EMG during maximum voluntary hand opening is reduced after SCI.
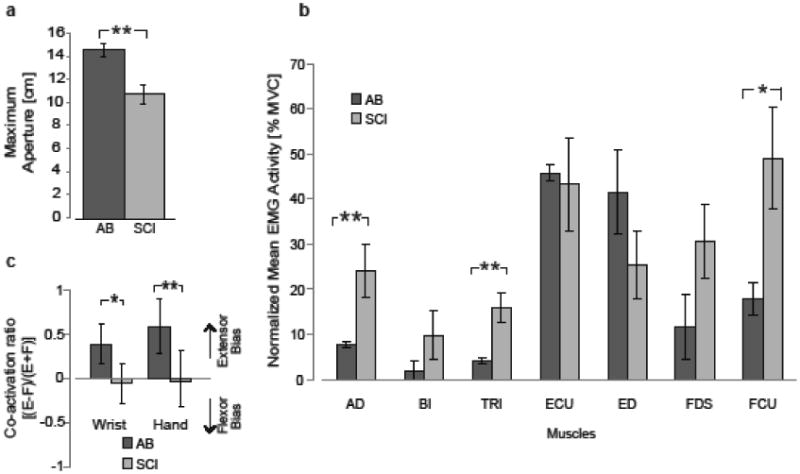
All bars represent mean ± 1 standard error. Statistical significance is indicated by an asterisk (p< 0.05) and double asterisk (p < 0.01) for between-group comparisons. (a) Mean maximum aperture was significantly greater for AB compared to SCI subjects. (b) Mean EMG activity across all subjects in the AB and SCI groups for a 100ms period that occurs 100ms prior to maximum aperture. EMG activation is normalized to maximum voluntary contraction (MVC) for each muscle and subject. SCI subjects show greater activation of proximal arm and hand flexor muscles. In (c), co-activation ratio represents the relative activation of flexors and extensors at the wrist or hand. Positive values represent greater proportional extensor (E) activity, while negative values represent greater flexor (F) activity. SCI subjects use more equal co-activation of flexors and extensors, while AB subjects use task-appropriate extensor-biased activity.
