Figure 3. Effect of sequence alterations in C4 domain on phosphorylation and protein interaction.
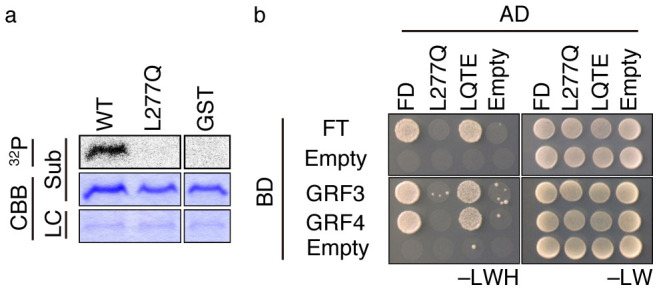
(a) In vitro kinase assay with wild-type (WT) or L277Q versions of C4 peptide (Fig. 1a) fused to GST or GST alone as a substrate.32P and CBB panels show autoradiography and Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) staining images of parts of the gel. Substrate (Sub) and loading control (LC, showing a band around the molecular mass of RubisCO large subunit) panels indicate that similar amounts of substrates and protein extracts from shoot apices of Day 7 plants, respectively, were used in the experiment. (b) Effect of sequence alterations in the C4 domain on the interaction with FT and 14-3-3s, examined by yeast two-hybrid assay. Wild-type (FD), L277Q, and LQTE (L277Q T282E) versions of FD were tested for an interaction with FT and two isoforms of 14-3-3, GRF3 (14-3-3 psi) and GRF4 (14-3-3 phi). AD and BD indicate the activation domain and DNA binding domain, respectively, of GAL4. –LWH and –LW indicate selective (SCD –Leu, –Trp, –His) and non-selective (SCD –Leu, –Trp) medium, respectively.
