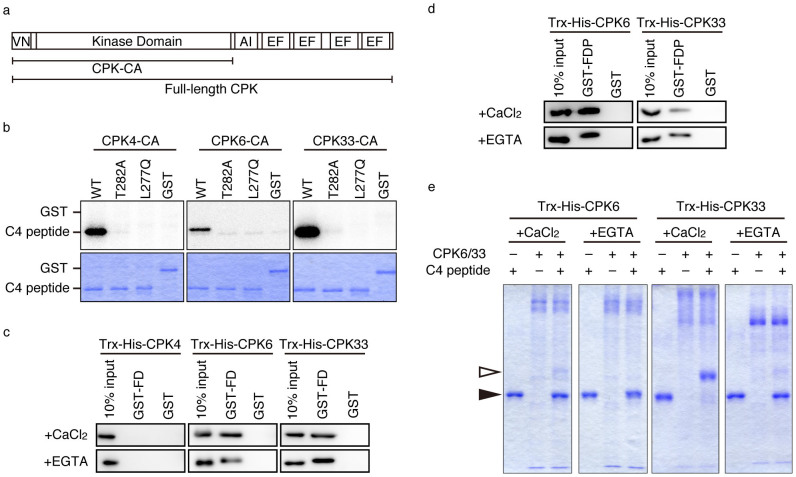
Figure 4. Biochemical characterization of candidate CDPKs.
(a) Domain structure of CDPK and fragments used in this study. VN: variable N-terminal domain, AI: auto-inhibition domain, EF: EF hand motif. CPK-CAs were constructed based on published information38 and primers used for cloning are shown in Table S2. (b) In vitro phosphorylation of FD T282 by CPK-CAs. Wild-type (WT), T282A, and L277Q versions of C4 peptide (Fig. 1a) or GST were used as substrates. Lower panels (CBB staining) confirm similar amounts of substrates in the experiments. Uncropped images of autoradiograms are shown in Supplementary Fig. S5a. (c) In vitro pull-down assay. Trx-His-CPKs were pulled-down with either GST-FD or GST in the presence (+CaCl2) or absence (+EGTA) of Ca2+. Immunoblot with anti-His tag antibody. One-tenth volumes of the reactions were loaded in “10% input” lanes. Uncropped images are shown in Supplementary Fig. S6a (upper panels). Results of immunoblotting with anti-GST antibody are also shown in Supplementary Fig. S6a (lower panels). (d) In vitro pull-down assay. Trx-His-CPKs were pulled-down with either GST-FDP or GST in the presence (+CaCl2) or absence (+EGTA) of Ca2+. Immunoblot with anti-His tag antibody. Ten percent, by volume, of the reactions were loaded in “10% input” lanes. Uncropped images are shown in Supplementary Fig. S6b (upper panels). Results of immunoblotting with anti-GST antibody are also shown in Supplementary Fig. S6b (lower panels). (e) Calcium-dependency of kinase activity of CPK6 and CPK33. In vitro phosphorylation reactions used full-length purified CPK6 and CPK33. WT C4 peptide was used as a substrate. Phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated C4 peptides were separated by Phos-tag SDS-PAGE. White and black arrowheads indicate phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated C4 peptide, respectively.