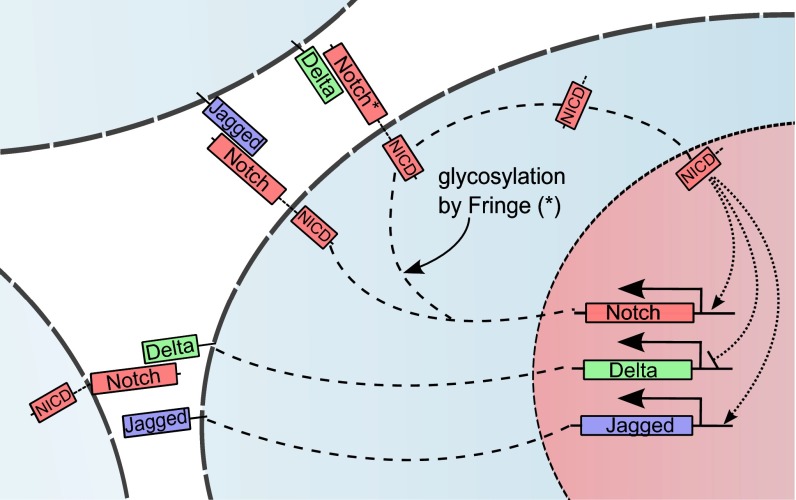
Fig. 1.
Overview of the intracellular and intercellular Notch signaling pathway. Notch, the transmembrane receptor of one cell, binds to Delta or Jagged, the transmembrane ligands belonging to the neighboring cell. This trans-interaction cleaves the Notch receptor to release NICD. NICD migrates to the nucleus and modulates the transcription of many genes. This modulation indirectly leads to the transcriptional activation of Notch and Jagged and inhibition of Delta. Interaction between Notch receptor and ligands (Delta or Jagged) of the same cell (cis-interaction) leads to the degradation of both the receptor and the ligand. Glycosylation of Notch by Fringe modifies Notch to have higher affinity for binding to Delta and lower affinity for binding to Jagged.