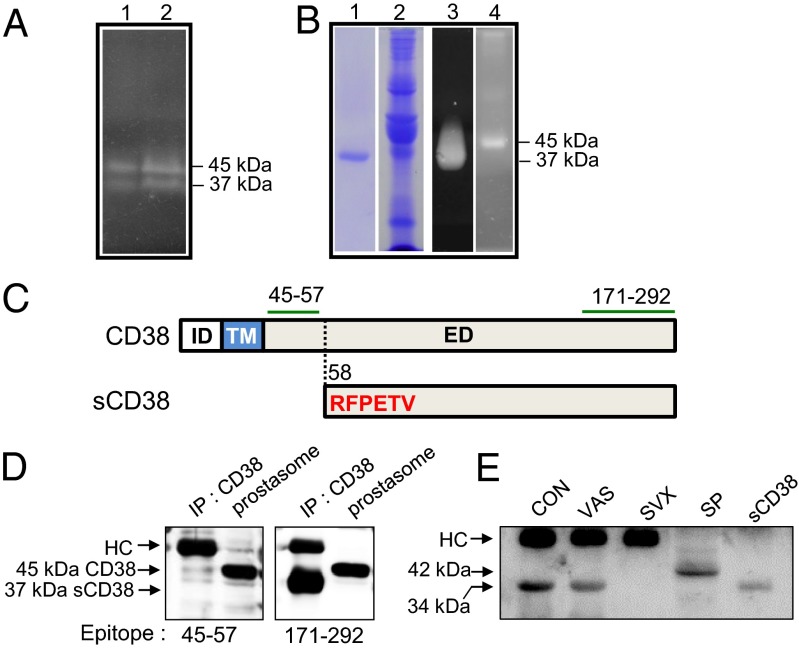
Fig. 1.
Identification of sCD38 in seminal fluid by in-gel ADPRC assay. (A) Visualization of human seminal fluid proteins with ADPRC activity (lanes 1 and 2 for two healthy volunteers). (B) Coomassie blue staining of proteins eluted from a CD38 immunoaffinity column (lane 1) and proteins that passed through the column (lane 2). In-gel ADPRC activity assay for the proteins eluted from the column (lane 3) and passed through the column (lane 4). (C) Upper diagram shows the intracellular domain (ID), TM domain, and extracellular domain (ED) of CD38, and the lower diagram shows the N-terminal amino acid (aa) sequence (highlighted in red) of sCD38. The segments (aa 45–57 and aa 171–292) denoted by green lines represent epitopes of the antibodies used for immunoblotting. The dotted line indicates the cleavage site within CD38. (D) Proteins immunoprecipitated from seminal fluid and prostasome lysates using anti-CD38 antibodies were blotted with antibodies specific for two different epitopes: amino acids 45–57 and 171–292. HC, heavy chain of Ig. (E) Mouse seminal plasma was collected from B6 females by uterine lavage within 1 h of mating with B6 intact (CON), vasectomised (VAS), and SVX males immunoprecipitated with anti-CD38, and the immunoprecipitates were analyzed for CD38 by Western blotting. Mouse splenocyte lysate (SP) and recombinant mouse sCD38 (sCD38) were included in the experiment as size references of full length and truncated sCD38.