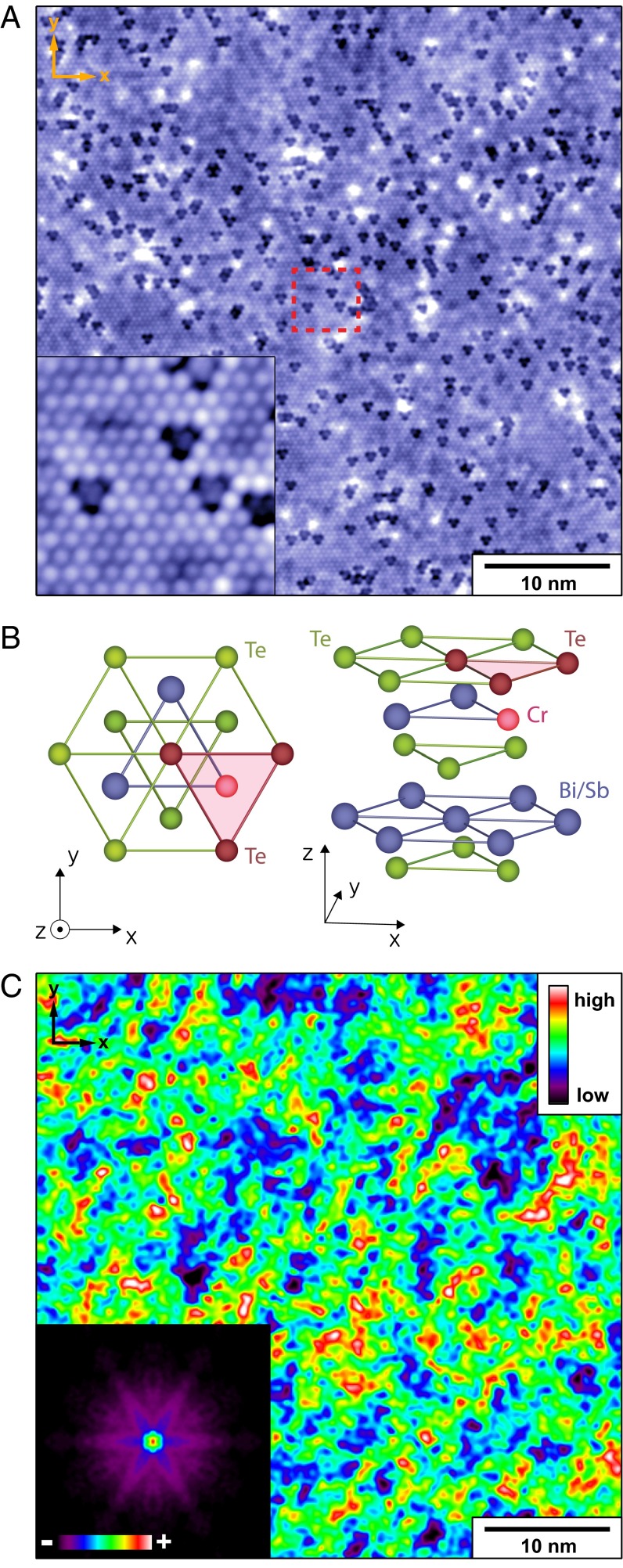
Fig. 1.
Cr dopant-atom locations at the TI surface. (A) Topographic image T(r) of Cr0.08(Bi0.1Sb0.9)1.92Te3 surface in a 47 × 47-nm2 field of view (FOV). Inset shows zoomed-in topographic image of red dashed-box area. Both images were measured at 10 pA/−200 meV. A single Cr dopant atom exists substituted at the Bi/Sb site at the symmetry point of every dark triangle in T(r) as discussed in B. (B) Schematic of the crystal structure of Crx(Bi0.1Sb0.9)2-xTe3. Each substitutional Cr atom is located at a Bi/Sb site at the symmetry point of a triangle of surface Te atoms (A). (C) Measured differential conductance g(r, E = −50 meV) in the same FOV as A. Inset shows spectral-density Fourier transform of the r-space differential conductance image showing the q-space signature of Friedel oscillations due to scattering interference of the surface-state electrons.