Fig 2.
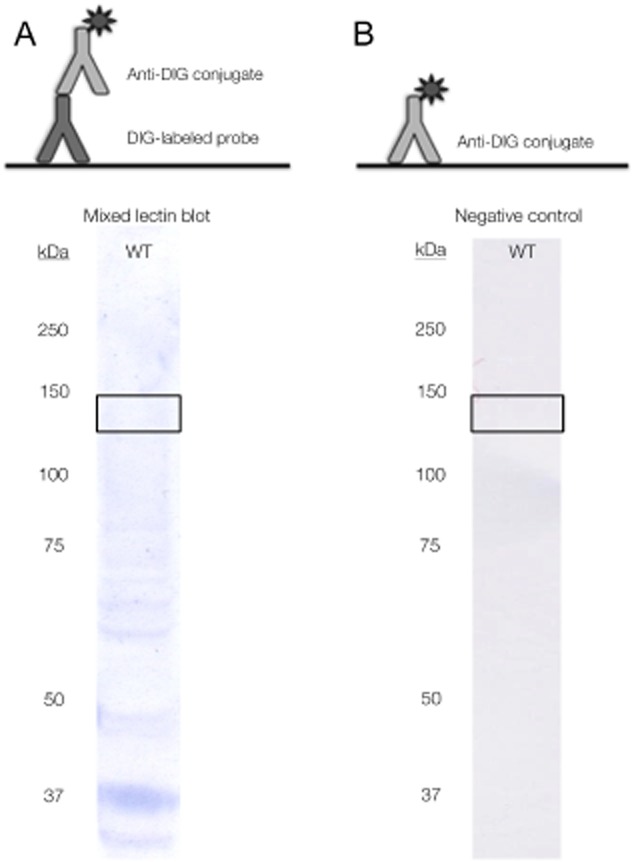
The digoxigenin–anti-digoxigenin detection as an alternative to avoid false positive hits caused by proteins binding endogenous biotin.A. DIG-labelled lectin blots – The wild type exoproteome of L. rhamnosus GG was Western blotted and developed using a mix of DIG-labelled lectins: ConA (Glc, Man), GNA (Man), HHA (Man), WGA (GlcNAc), DSL (GlcNAc), UDA (GlcNAc), Nictaba (GlcNAc), RSA (Gal, GalNAc) and PNA (Gal, GalNAc). These lectins were labelled using digoxigenin-3-O-methyl-ε-aminocaproix acid-N-hydroxysuccinimide ester (Roche). Anti-DIG Fab antibody fragments (Roche) were used to detect proteins that reacted positively with the lectin probes. Here, we clearly see that the false positive band at 125 kDa is absent.B. Negative control with anti-DIG – Direct application of the anti-DIG Fab antibody fragments (Roche) to the Western blotted proteome of L. rhamnosus GG results in a blot on which no bands can be perceived. This confirms that the DIG–anti-DIG detection method is a good alternative for the biotin–streptavidin system, without causing false positive hits.
