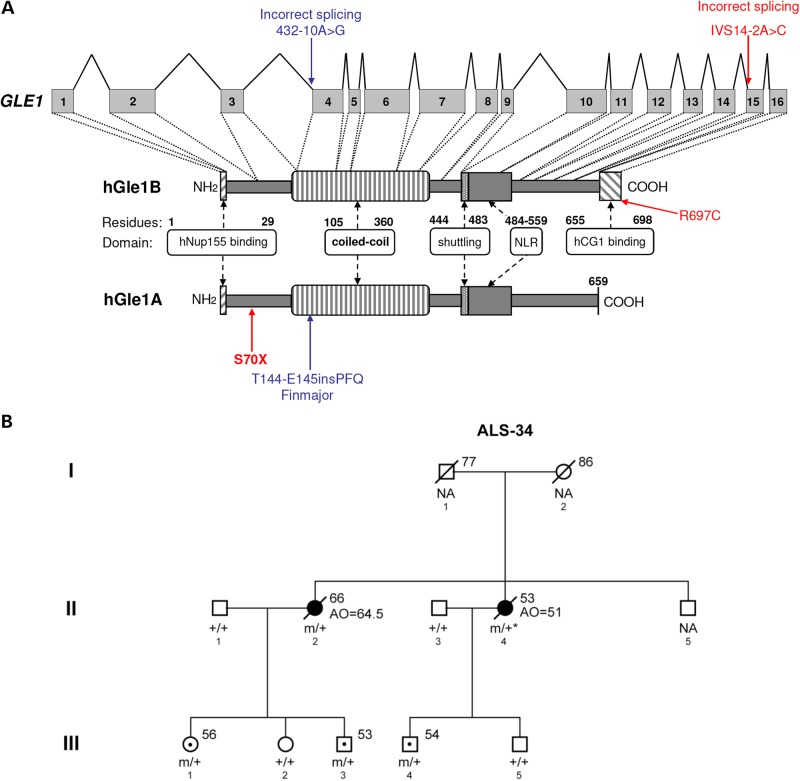
Figure 1.
Identification of GLE1 mutations in ALS patients. (A) Structure of GLE1 gene and hGle1A and hGle1B proteins. Amino acid residues of known functional domains are indicated [adapted from Kendirgi et al. (8)]. Locations of identified changes are shown in red for ALS patients and blue for LCCS1 GLE1-FinMajor mutation. (B) Familial ALS-34 pedigree containing the GLE1-c.1965-2A>C mutation that encodes the hGle1-IVS14-2A>C protein. Genotypes of analyzed family members are indicated (squares, males; circles, females; black symbols, affected individuals; symbols with central dot, unaffected mutation carriers; slash marks, deceased individuals; ‘+’, WT; ‘m’, mutant; ‘NA’, no DNA sample available; asterisk, inferred genotype; numbers to the upper right of individual family members indicate age at death/current age).