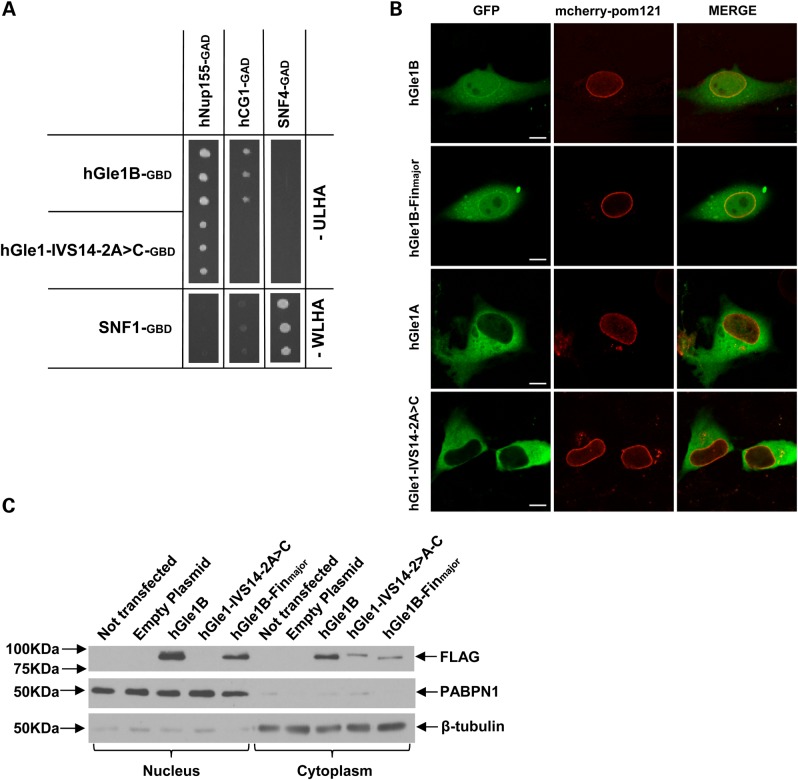
Figure 4.
Cellular localization and interactions of the hGle1-IVS14-2A>C mutant protein. (A) Yeast-2 hybrid analysis for the ability of the hGle1-IVS14-2A>C mutant protein to interact with hNup155 and hCG1. Interactions were detected by growth on media lacking uracil, leucine, histidine and adenine (-ULHA) (for hGle1B-GBD and IVS14-2A>C-GBD) or lacking tryptophan, leucine, histidine and adenine (-WLHA) (for SNF1-GBD control). (B) Live-cell imaging of HeLa cells transfected with WT or mutant GFP-tagged GLE1 constructs and mcherry-tagged Pom-121 (nuclear envelope/NPC marker); scale bar: 10 μm. (C) Western blot of nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins from HeLa cells transfected with FLAG-tagged WT or mutant GLE1 constructs, probed with antibody against FLAG. PABPN1 and β-tubulin represent nuclear and cytoplasmic loading controls, respectively.