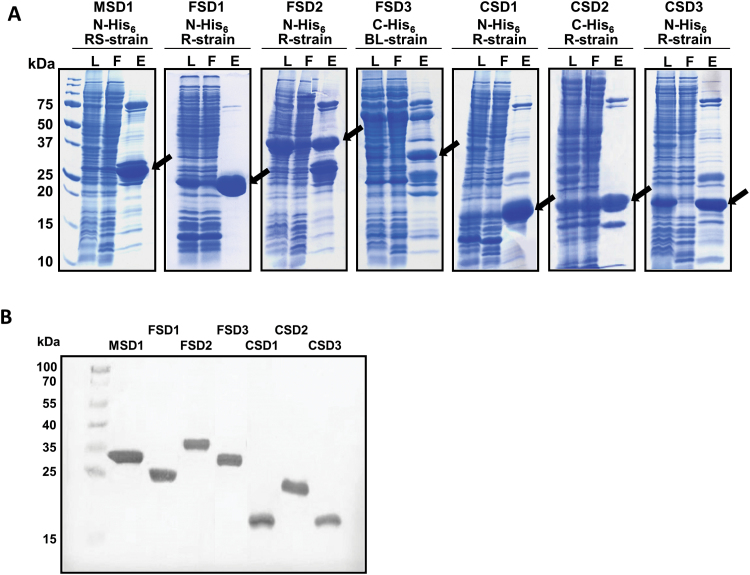
Fig. 1.
Production, purification, and detection of recombinant Arabidopsis SODs. (A) The coding sequences of the different Arabidopsis SODs were cloned into pDEST17 (N-terminal His6) or pDEST42 (C-terminal His6) using the Gateway Technology. Three different bacteria production strains (RS-strain=Rosetta DE3 pLysS; R-strain=Rosetta DE3; BL-strain=BL21 DE3) were tested and the most productive one for each isoform was used. His-tagged SODs were purified by Ni–NTA affinity chromatography. Crude bacterial lysate (L), flow-through (F), and eluate (E) were separated by SDS-PAGE and visualized by Coomassie Blue staining. Arrows indicate the produced SOD isoforms. The relative mass of protein standards are shown on the left. (B) Detection of purified, recombinant Arabidopsis SOD isoforms. Eluates containing recombinant SOD isoforms were separated by SDS-PAGE and blotted onto nitrocellulose membrane. Detection of His-tagged proteins was achieved using anti-His antibody. The relative mass of protein standards are given on the left. (This figure is available in colour at JXB online.)