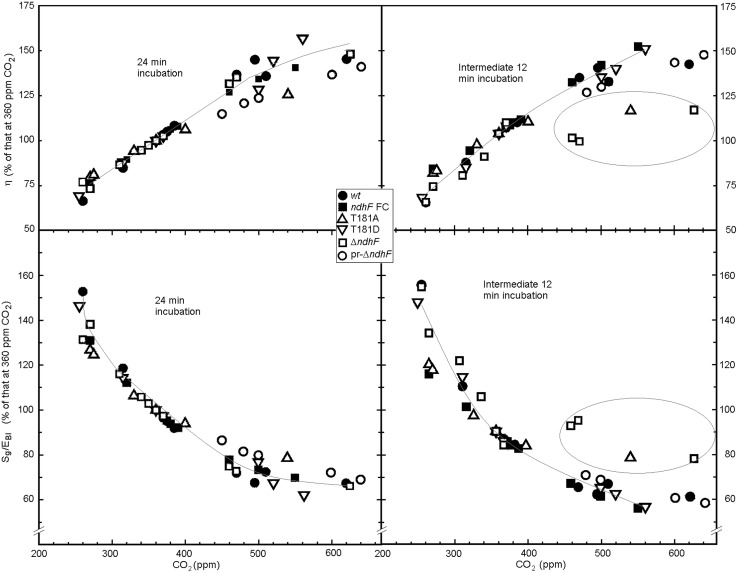
FIGURE 4.
Effect of the concentration of CO2 on photosynthetic efficiency (η) and Sg/EBI of different tobacco plants. As explained in the thermodynamic background, photosynthetic efficiency is the ratio of chemical energy (EBI) stored as photosynthesized biomass to the PAR energy absorbed by the leaf. Sg/EBI is the ratio of the total entropy produced to the chemical energy (EBI) stored as photosynthesized biomass. Calculations were performed for the total 24 min (left boxes) and the 12 min intermediate (right boxes) light incubation treatments. The represented values of η and Sg/EBI at different CO2 concentrations are the percentages with respect to corresponding values at 360 ppm CO2 (references at 360 ppm are in the range of 3.6% η and 0.08 K-1 Sg/EBI for all plants). The concentrations of CO2 represented are those determined by the LCpro+ photosynthesis system in the leaf chamber and could slightly change with respect to those programmed. As repeated determinations for very similar CO2 concentrations in a same tobacco produced very close points, only the mean value is represented. Therefore, points in the figure result from 139 different assays and several are the mean of 2–4 independent determinations. Inserted gray lines were obtained by second degree polynomial fitting of the experimental points corresponding to wt, ndhF FC, T181D tobacco plants that contain full dose of functional ndhF gene. Encircled points in left boxes correspond to those of ΔndhF and T181A at high CO2 concentrations.