Fig. 5.
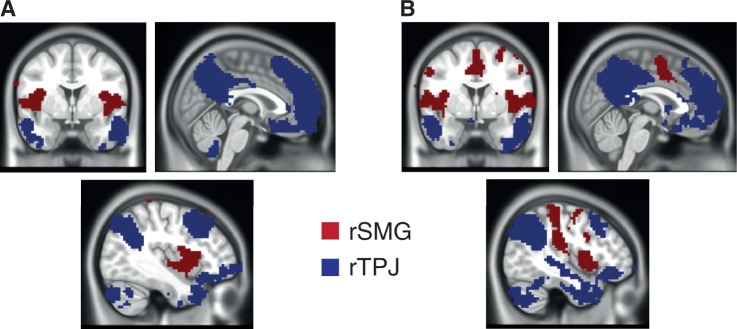
Functional connectivity differences between rSMG and rTPJ in children and adults (pfwe < 0.05). (A) In adults, rSMG showed more marked connectivity relative to rTPJ to bilateral insula and rSMG; conversely, rTPJ was more strongly connected than rSMG to large portions of medial PFC, precuneus, TPJ, the temporal poles and superior frontal gyrus. (B) For children, these patterns were virtually identical, with the exception of increased connectivity between rSMG and medial cingulate cortex.
