Figure 3.
Antiviral effect of CsA-encapsulated poly (glycolic-co-lactic) acid nanoparticles in vitro.
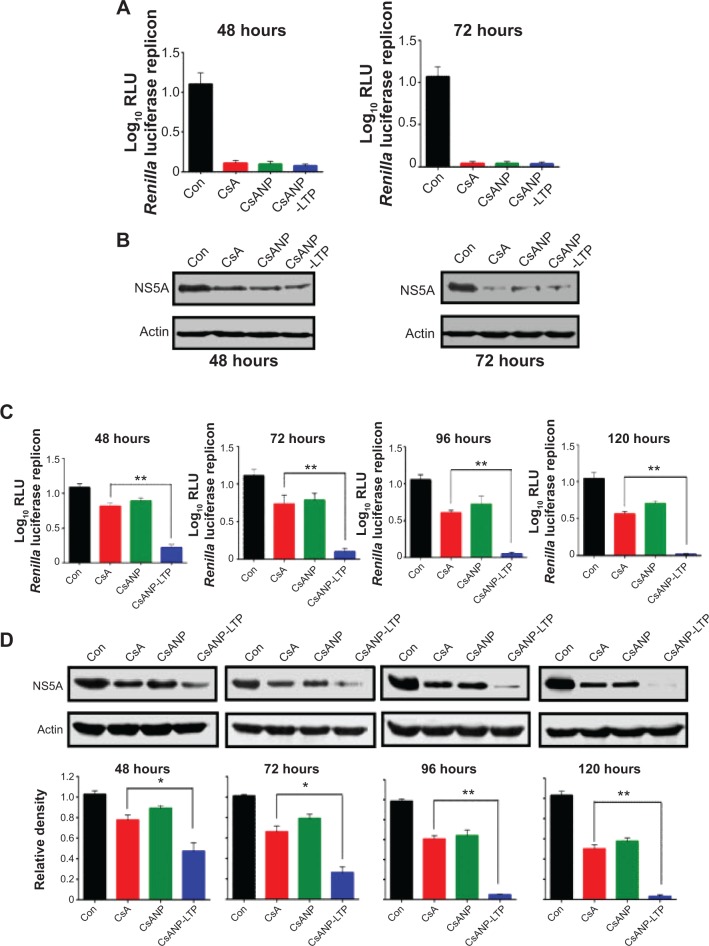
Notes: (A) HCV replicon cells were treated with 2.5 μg of CsA, CsANP, or CsANP-LTP for different time intervals, and luciferase activity was determined. The data are shown as the mean ± SD. (B) HCV NS5A expression levels were determined by Western blot analysis after HCV replicon cells were incubated with 2.5 μg of CsA, CsANP, or CsANP-LTP for different time intervals. All data are representative of three individual experiments. The sustained anti-HCV effect of CsA from targeted nanoparticles was determined by treatment-withdrawal experiments in HCV replicon cells. After 12 hours of treatment with 2.5 μg of CsA, CsANP, or CsANP-LTP, the cells were replaced with fresh culture medium followed by culturing for different time points. (C) Luciferase assay. The data are shown as the mean ± SD. **P<0.01 versus CsA treatment. (D) Western blot analysis of HCV NS5A expression levels. Actin was used as loading control. The density values of HCV NS5A relative to actin are expressed as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 versus CsA treatment.
Abbreviations: Con, control group; CsA, cyclosporine A; CsANP, cyclosporine A nanoparticles; CsANP-LTP, CsANP conjugated with liver-targeting peptide; HCV, hepatitis C virus; RLU, relative light units; SD, standard deviation.