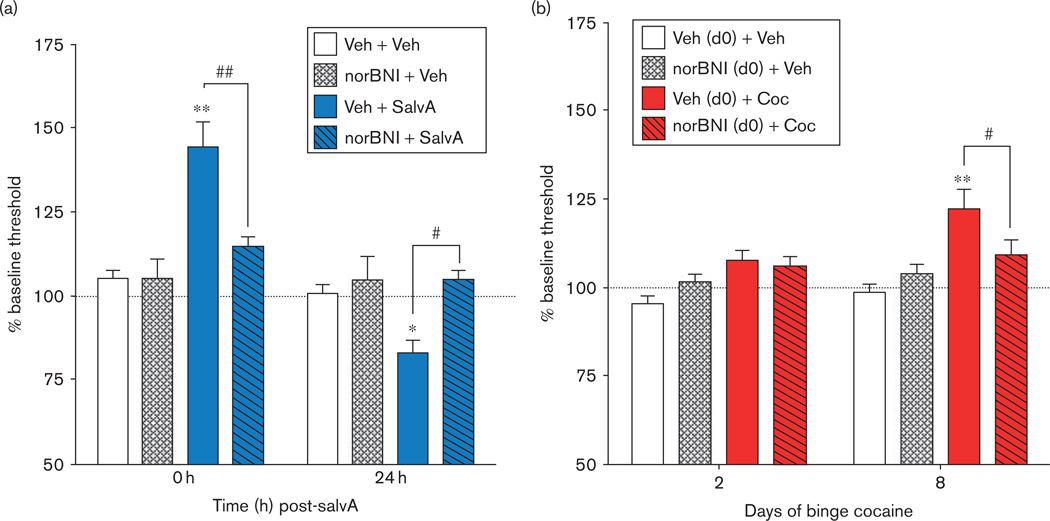
Fig. 2.
Evidence that processes that have an affective valence are followed in time by an opponent process that has the opposite valence. Hedonic states are determined by intracranial self-stimulation (ICSS). An increase in % baseline threshold [lowest frequency (Hz) of stimulation at which rats will perform operant behavior] reflects a decrease in sensitivity to brain stimulation reward (i.e. anhedonia), whereas a decrease in % baseline threshold reflects an increase in sensitivity to brain stimulation reward. (a) Rats treated with salvinorin A (salvA, 2.0 mg/kg, intraperitoneally) show an immediate (0 h post injection) increase in ICSS thresholds and a delayed (24 h post injection) decrease in ICSS thresholds compared with vehicle-treated rats (Veh, 75% dimethyl sulfoxide). Both are sensitive to blockade by the κ-opioid receptor (KOR) antagonist norBNI (10 mg/kg, intraperitoneally, given 24 h before salvA; adapted with permission from Potter et al., 2011). (b) Rats treated with cocaine (Coc) in a binge-like regimen (3× 15 mg/kg/day for 14 days, intraperitoneally) show normal ICSS thresholds 21 h after the first day of cocaine injection but develop increased ICSS thresholds compared with vehicle-treated rats (Veh, 0.9% saline), which plateau after ~8 days of binge treatment. Treatment with norBNI [20 µg, intracerebroventricularly, day 0 (d0), 24 h before the start of the cocaine binge regimen] prevents cocaine withdrawal-induced anhedonia (adapted with permission from Chartoff et al., 2012). *P < 0.05, **P <0.01 compared with Veh +Veh; #P< 0.05, ##P<0.01 comparing groups under the bars.