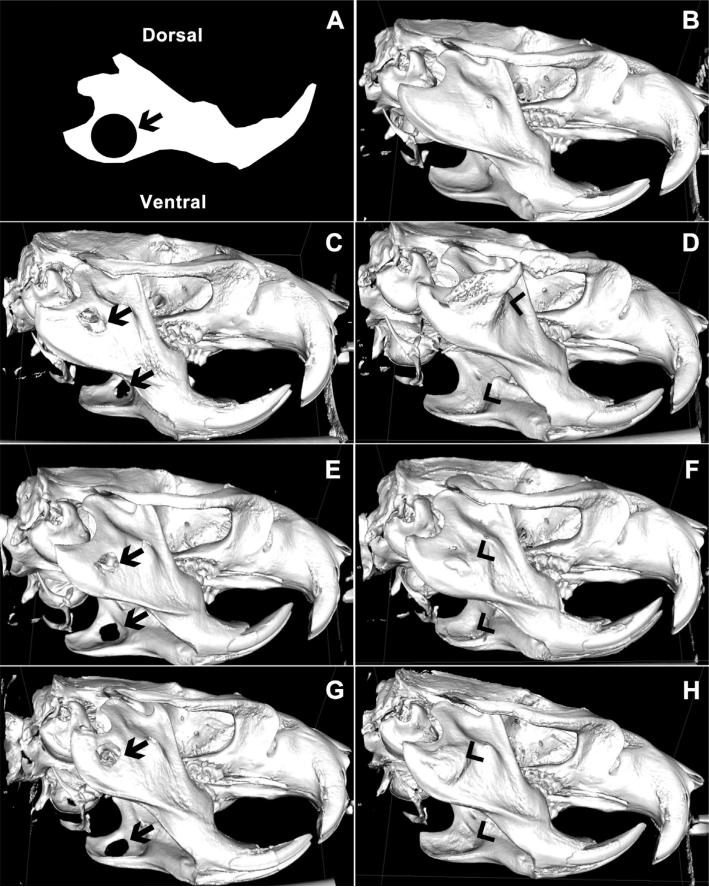
Fig. 4.
(A) Schematic of initial 5 mm defect size and location imposed on a sketch of a normal rat mandible. (B–H) Representative μCT images of bone regeneration sixteen weeks after surgical creation of a bilateral 5 mm critically-sized circular mandibular defect in (B) normal, uninjured, age-matched mandible, (C) rats receiving no treatment, (E) kerateine gel without rhBMP-2 or (G) kerateine scaffold without rhBMP-2 were unable to bridge the defect (arrows). Administration of (D) ACS with 5 μg rhBMP-2, (F) kerateine gel with 5 μg rhBMP-2, or (H) kerateine scaffold with 5 μg rhBMP-2 were able to close the defect with varying degrees of undesired ectopic bone growth (arrowheads).