Fig. 2.
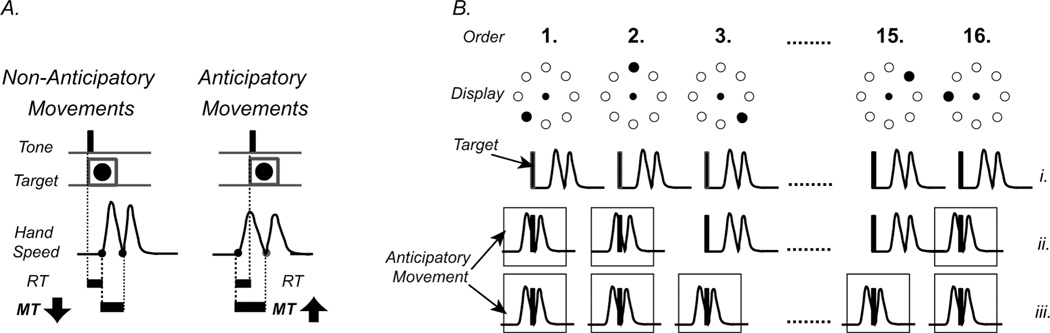
A. Anticipatory and Non-Anticipatory Movements. Anticipatory Movements have RT below the lowest reaction time achieved in RAN as well as longer Movement Time (MT) and lower peak velocity compared to Non-Anticipatory Movements. B. Development of anticipatory movements during a 16-element sequence: In the beginning of the learning process, (i) Movements are initiated in response to target presentation. Soon, (ii) some movements become anticipatory (boxed hand-paths). Finally, (iii) when the whole sequence is acquired, all targets are anticipated.