Figure 5.
Structural Analysis of NEMF Interactions on the 60S-RNC
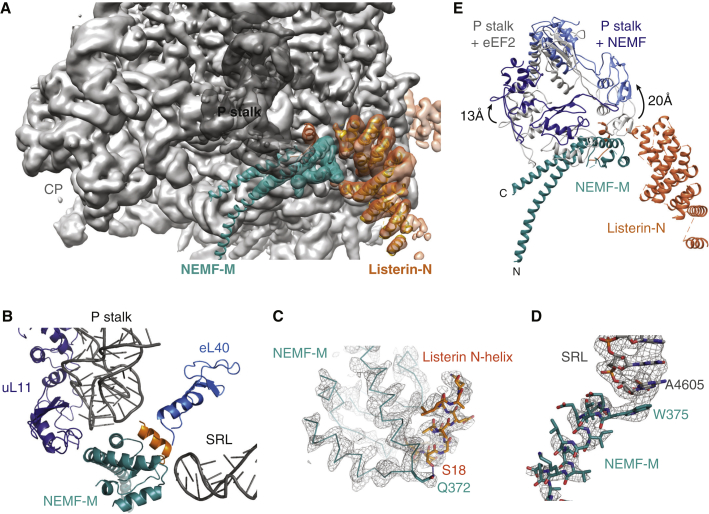
(A) Side view of the N terminus of Listerin (orange) contacting NEMF (teal) and the 60S subunit (gray) with density for the P stalk in dark gray. De novo models of NEMF’s M-domain and Listerin’s N-terminal helix, along with a poly-alanine model of the helices of Listerin’s N-terminal HEAT repeats is superimposed into the density (filtered at 5 Å).
(B) Atomic models of the middle domain of NEMF (NEMF-M, teal), the N-terminal helix of Listerin (orange), eL40 (light blue), uL11 (dark blue), and interacting portions of the 28S rRNA (dark gray).
(C) De novo built models of the NEMF-M domain and Listerin's N-terminal helix fit to map density, illustrating a likely interaction.
(D) Models fitted to map density illustrating a stacking interaction of W375 of the NEMF-M domain with A4605 of H95/sarcin-ricin loop of the 28S rRNA.
(E) View of the M-domain of NEMF (teal) with corresponding positions of the P stalk proteins uL11 (dark blue) and uL10 (light blue) in the map of the 60S subunit in complex with NEMF and Listerin (blue) or of the same proteins in a map of an 80S ribosome bound to eEF2 (gray).