Figure 4. ASC deficiency significantly increases bacterial colonization and delays genital C. muridarum infection clearance, while NLRP3 has a marginal effect and NLRC4 deficiency has no effect.
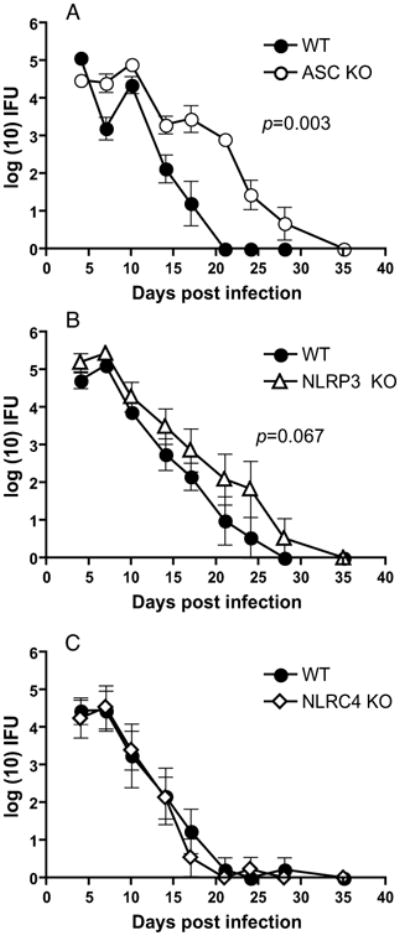
C. muridarum infection course in (A) WT (N=5) and ASC KO (N=5), (B) WT (N=5) and NLRP3 KO (N=5) mice, and (C), WT (N=10) and NLRP3 KO (N=10) mice. Log10 (IFUs/ml) were calculated from genital swabs as described in Methods and graphed as means ± standard error of the means for animals positive for infection on that day. Significance was determined by two-way RM ANOVA (WT vs. ASC KO, p =0.003; WT vs. NLRP3 KO, p < 0.067). Kaplan-Meier survival analysis showed a significance of p= 0.005 for WT vs. ASC KO mice clearing infection. A representative of 3 experiments is shown.
