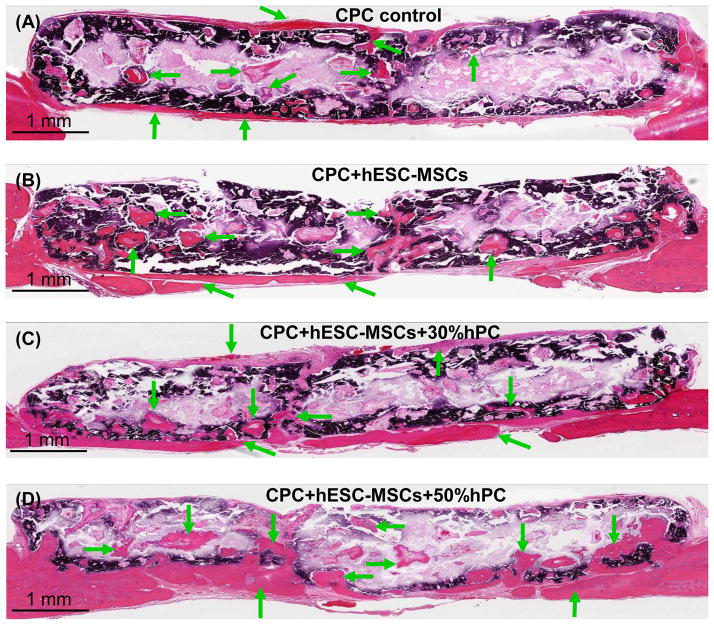
Figure 4.
Typical H&E images of the cross-sections of the critical-sized cranial defects in rats at 12 weeks. (A) CPC scaffold control without cells; (B) CPC seeded with hESC-MSCs (referred to as “CPC+hESC-MSC”; (C) CPC+hESC-MSC+30%hPC; and (D) CPC+hESC-MSC+50%hPC. Arrows indicate areas of new bone. There was more new bone in the groups with hESC-MSCs than CPC control without cells. There was more new bone when hPC was used, compared to that without hPC. The dark purple and white areas are residual CPC (the white areas were due to detachment of CPC during sample preparation). The dark purple staining of CPC was caused by incomplete decalcification in the CPC blocks during sample preparation.