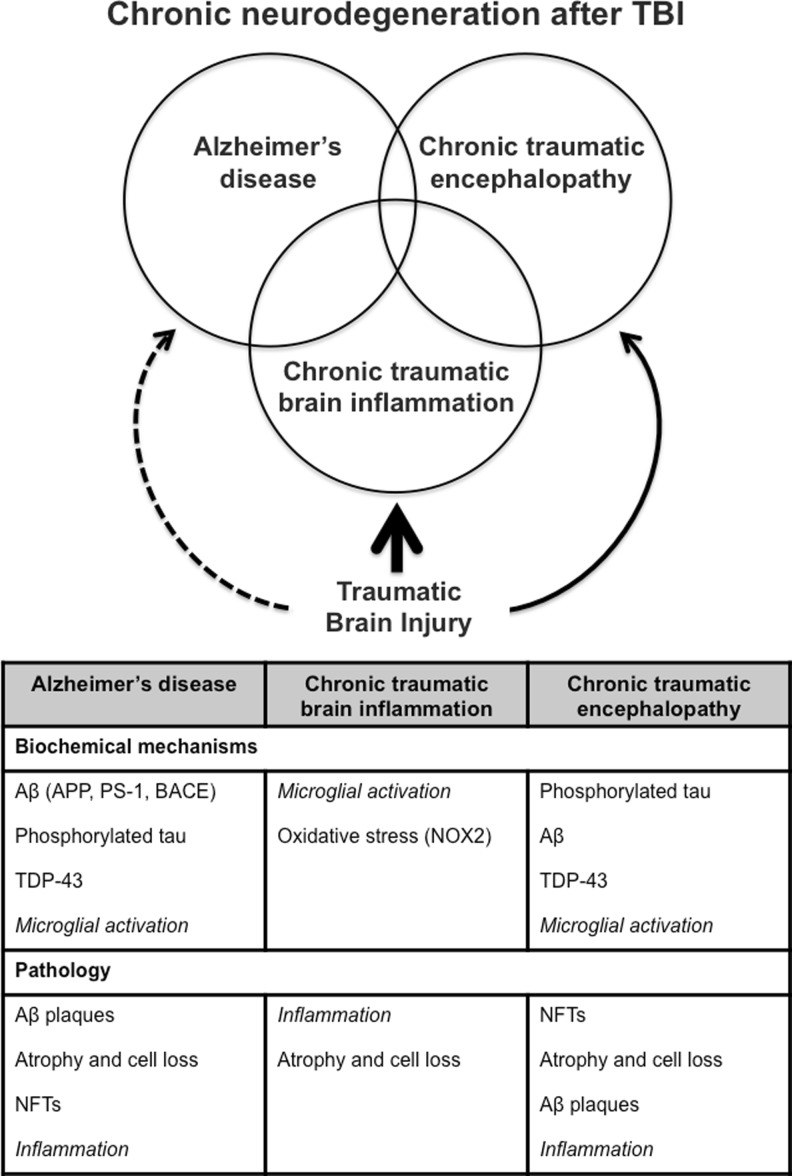
Fig. 1.
Chronic neurodegeneration after traumatic brain injury (TBI)—a complex and multifactorial pathobiology. Single or repeated TBI initiates complex biochemical mechanisms that lead to chronic neurodegeneration and delayed chronic neuropsychiatric changes. The biochemical and pathological features of Alzheimer’s disease, chronic traumatic brain inflammation, and chronic traumatic encephalopathy following TBI are shown. Aβ = β-amyloid; APP = amyloid precursor protein; PS-1 = presenilin-1; BACE = β-amyloid converting enzyme; TDP-43 = TAR DNA-binding protein 43; NFTs = neurofibrillary tangles; NOX2 = NADPH oxidase