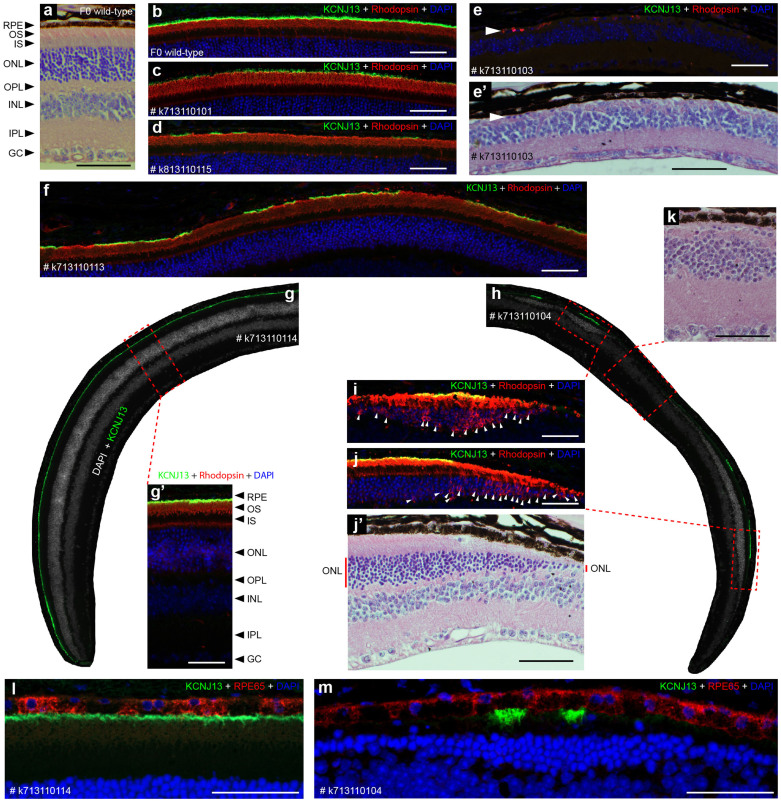
Figure 3. CRISPR-Cas9-induced F0 mosaic loss of KCNJ13 in RPE cells causes photoreceptor disease phenotypes.
Protein expression of KCNJ13 is shown in green, rhodopsin and RPE65 are shown in red. DAPI (blue) marks nuclei. The loss of photoreceptor cells was determined by comparing the thickness of the ONL between mutant and wild-type mice. (a) A cross-section of a F0 wild-type eyecup stained with H&E is shown. (b) KCNJ13 expression in wild-type RPE cells and rhodopsin localization in the outer segment (OS) of photoreceptor cells are shown. Images a and b are from adjacent serial sections of the same F0 wild-type eyecup prepared from an animal at 13 weeks of age. (c,d,e,f,g,h) KCNJ13 mosaic expression and rhodopsin localization in retinas prepared from animals at 13 weeks (c,d), 17 weeks (e), 22 weeks (f), and 33 weeks of age (g,h). Each image represents one mosaic mutant mouse (each unique ID is included with each image). (i,j,k) Loss of photoreceptor cells (i,k) and accompanied rhodopsin mislocalization, indicated by white arrowheads (i,j). Images e and e’, as well as j and j’, are taken from similar regions of adjacent serial sections. k and j’ are from the same H&E stained section and show that retinal morphology and loss of photoreceptor cells correlates with regions lacking KCNJ13 protein. (l,m) Co-staining of KCNJ13 and RPE65 to demonstrate that mutant RPE cells are surviving. RPE, retinal pigment epithelium. OS, outer segment. IS, inner segment. ONL, outer nuclear layer. OPL, outer plexiform layer. INL, inner nuclear layer. IPL, inner plexiform layer. GC, ganglion cell. Scale bar is 50 µm.