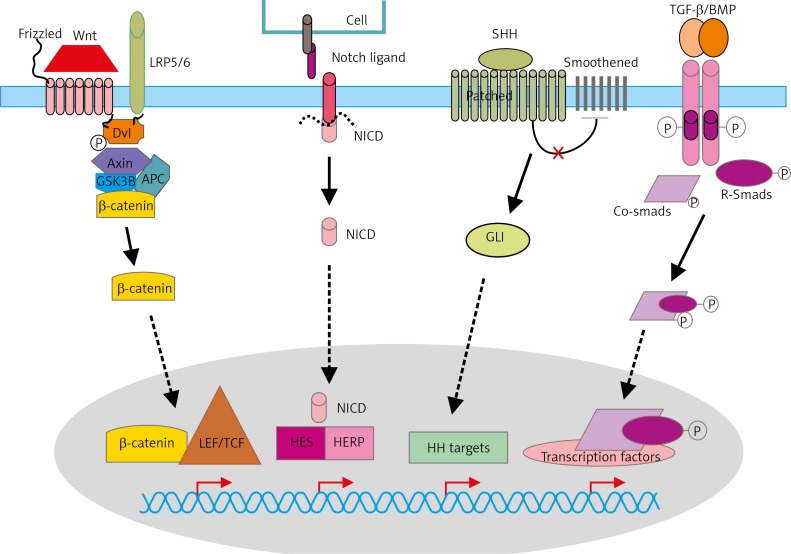
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of signalling pathways that control maintenance of BCSCs
Wnt binds its co-receptors: Frizzled (Fz) and LRP5/LRP6. Various molecules that interact with the receptors and GSK-3 and CK1 (casein kinase 1). In the presence of Wnt, β-catenin is stabilised and induces gene expression by complexing with various transcription factors such as TCF/LET. The Delta-like and the Jagged proteins produced by signal-sending cells serve as ligands for Notch receptors. Upon ligand binding, the receptor fragment is cleaved by TACE (TNF-α ADAM metalloprotease converting enzyme) then γ-secretase to create NICD (Notch intracellular domain), which translocates to the nucleus, forms a complex with transcription factors RBPJ and CSL (CBF1/Suppressor of Hairless/LAG-1), and activates the expression of target genes (f.e. Hes1 and Herp). Sonic Hedgehog (SHH) binds to a transmembrane protein Patched (PTCH), which constitutively represses Hh pathway activity through its interaction with a transmembrane protein Smoothened (SMO). Shh-bound PTCH activates SMO, and activated SMO releases GLI1 (Glioma-Associated Oncogene Homolog 1) from cytoplasmic sequestration, and, in turn, GLI1 translocates into the cell nucleus to regulate gene expression. Activation of TGF-β type I and type II receptors leads to activation of receptor kinases and phosphorylation of the R-Smads, forming a complex with co-Smad 4, which translocates to the nucleus