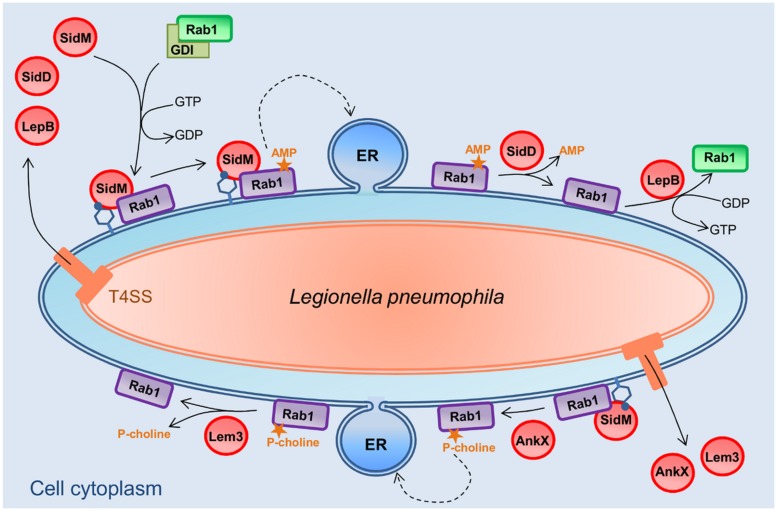
FIGURE 3.
Post-translational modifications of small GTPase Rab1 by L. pneumophila for LCV biogenesis. The ER recruitment on the LCV is orchestrated by four Dot/Icm effectors-mediated PTMs. SidM releases Rab1 from GDI with its GEF activity. SidM then modifies Rab1 by AMPylation, i.e., the addition of a AMP moiety. This PTM locks Rab1 in the GTP-bound active state, and finally allows ER recruitment at the surface of the LCV. SidD removes AMP from Rab1, making it accessible for GAP activities, such as that exhibited by LepB. LepB promotes GTP hydrolysis of Rab1, removing it from the LCV. AnkX harbors a novel PTM activity, the phosphocholination, that transfers a phosphocholine moiety to Rab1, resulting in the same effect that the SidM-mediated AMPylation, i.e., locking Rab1 in the active form. The Dot/Icm effector Lem3 possesses an antagonistic activity to that of AnkX by removing the phosphocholine from Rab1.