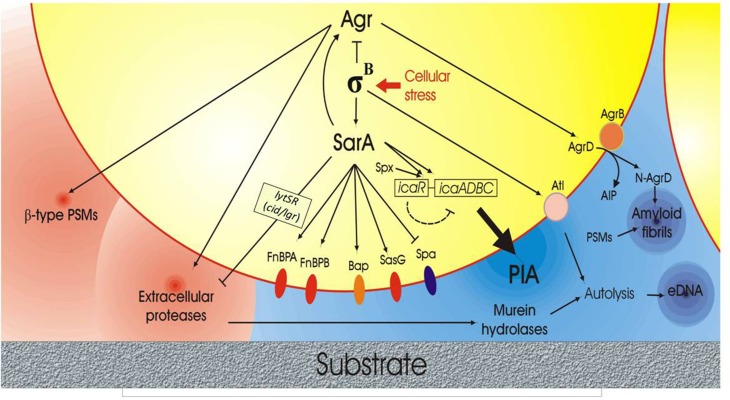
Figure 2.
Scheme of the complex network of interactions governing biofilm formation and disruption in S. aureus based on current scientific evidences. The right side of the figure illustrates the anabolic phase of biofilm with the production of some fundamental extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) such as PIA, extracellular-DNA (eDNA) and amyloid fibrils. The lytSR operon with its target genes lrg/cid, which affects murein hydrolase activity, is also represented. The center of the figure reports the protein membrane components implicated in biofilm formation, these including the FnBPs adhesins, the Biofilm associated protein (Bap), SasG and Spa. Conversely, in the left side of the figure, the molecules playing a role in biofilm catabolism and extracellular biofilm matrix disruption, such as phenol-soluble modulins (PSMs) and extracellular proteins, are reported. Agr QS system, σB factor and SarA appear to act as central regulators, orchestrating the bacterial behavior in response to stress factors, cellular densities and cell cycle phases.