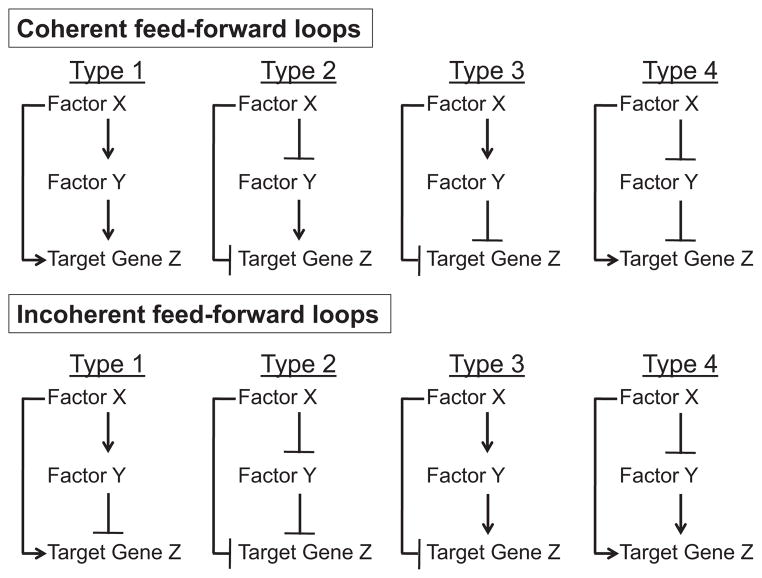
Fig. 1.
Structural configurations of the transcriptional feed-forward loop (FFL). The FFL consists of a primary transcription factor X, which regulates a secondary transcription factor Y, such that X and Y both individually and combinatorially regulate expression of target gene Z. Each of the three regulatory events can be positive or negative, providing for the 8 possible structural configurations of the FFL presented here. In this schematic, lines heading in arrowheads represent induction, and lines ending with a perpendicular dash indicate repression. The two most common types of transcriptional feed-forward networks of E. coli and yeast are the coherent-type 1 and incoherent-type 1 FFLs, depicted in the top left and bottom left panels, respectively. Each distinct connectivity pattern has been found/is predicted to confer unique response profiles to feed-forward target genes.