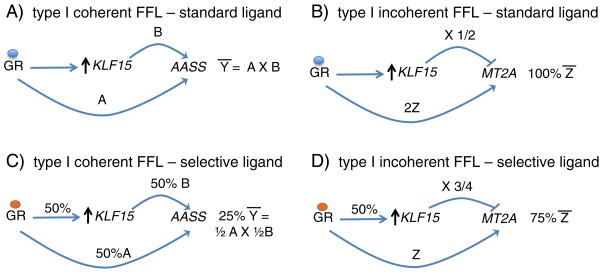
Fig. 2.
A simplified, theoretical model comparing the effects of a hypothetical selective GR ligand on the expression of a GR:KLF15 coherent feed-forward target, AASS, and a GR:KLF15 incoherent feed-forward target, MT2A. A. With a standard GR ligand, shown as a blue circle, AASS expression is induced to level Ȳ, based on the combinatorial activity of both GR and KLF15. B. Similar to A, MT2A is induced to level Z̄, which represents combined inductive effects of GR and repressive effects of GR-induced KLF15. C. Here, a selective GR ligand, shown as an orange circle, causes GR to induce 50% of the expression level of KLF15 and AASS that was achieved with the standard ligand. However, the final level of AASS expression is 25% Ȳ, since lower GR-induced KLF15 levels lead to further decreases in AASS expression. D. Here the putative effects of the selective GR ligand are shown on the expression of the incoherent feed-forward target, MT2A. In this case, reduced GR-mediated induction of KLF15 in part balances the reduced inductive effect of GR on MT2A, leading to 75% expression of MT2A.