Figure 2. Acidosis induces IκBα phosphorylation, IκBα degradation and p65 phosphorylation.
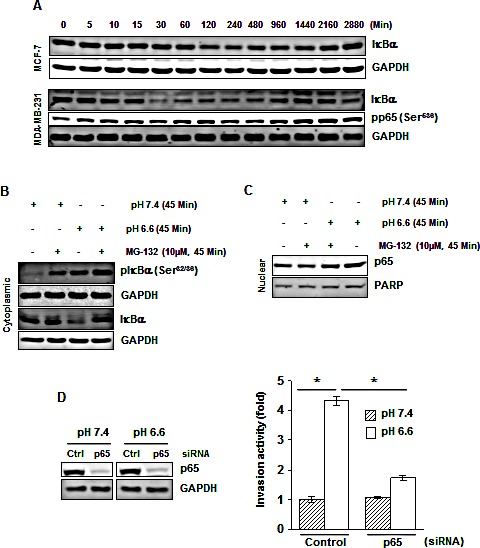
(A) Cells were cultured at pH 6.6 for the indicated times, cytoplasmic extracts were prepared and analyzed for IκBα and pp65 by Western blotting. (B) Acidosis induces IκBα phosphorylation in MDA-MB-231 cells. Cells were cultured at pH 7.4 or pH 6.6 in absence or presence of MG-132 for 45 minutes. Cytoplasmic extracts were analyzed by Western blotting using a phospho-specific IκBα (Ser32/36) and IκBα antibodies, and (C) Nuclear extracts were analyzed for p65. (D) Gene silencing of NF-κB-p65 abolishes acidosis induced invasion activity of MDA-MB-231 cells. (Left), cells were transfected with p65 siRNA and control siRNA in normal medium. After 24 h, cells were cultured under normal or acidic medium for 24 hours, and whole-cell extracts were analyzed by Western blotting using p65 antibody. (Right), the p65 silenced cells cultured under normal and acidic conditions were assessed in vitro for invasion activity using Matrigel chambers. *, p< 0.05.
