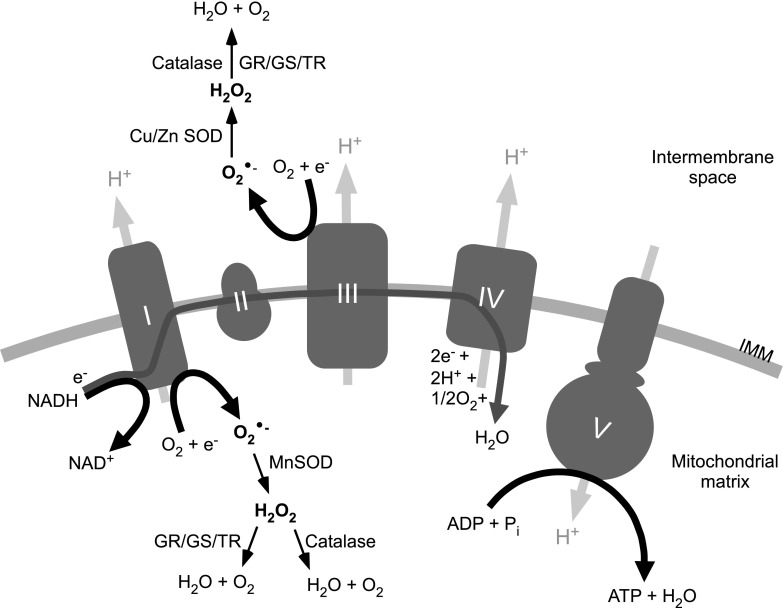
FIG. 2.
Schematic representation of ROS generation in mitochondria. The main sites of ROS generation within mitochondrial ETC are ETC complexes I and III (complexes I to V are represented by gray shapes and labeled accordingly). O2•− is formed by molecular oxygen reacting with the electrons from the ETC. In the mitochondrial matrix, O2•− is converted to H2O2 by MnSOD. H2O2 can then be reduced to H2O and O2 by catalase or through glutathione/thioredoxin reduction pathways. In the intermembrane space of mitochondria, O2•− can be generated at complex III, where it is reduced to H2O2 by CuSOD and ZnSOD. Based on the generalizations provided in Refs. (118, 196). IMM, inner mitochondrial membrane; GR, gluthathione reductase; GS, glutathione synthase; TR, thioredoxin; ETC, electron transport chain; MnSOD, manganese superoxide dismutase; CuSOD, copper superoxide dismutase; ZnSOD, zinc superoxide dismutase; ROS, reactive oxygen species; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; O2•−, superoxide anion.