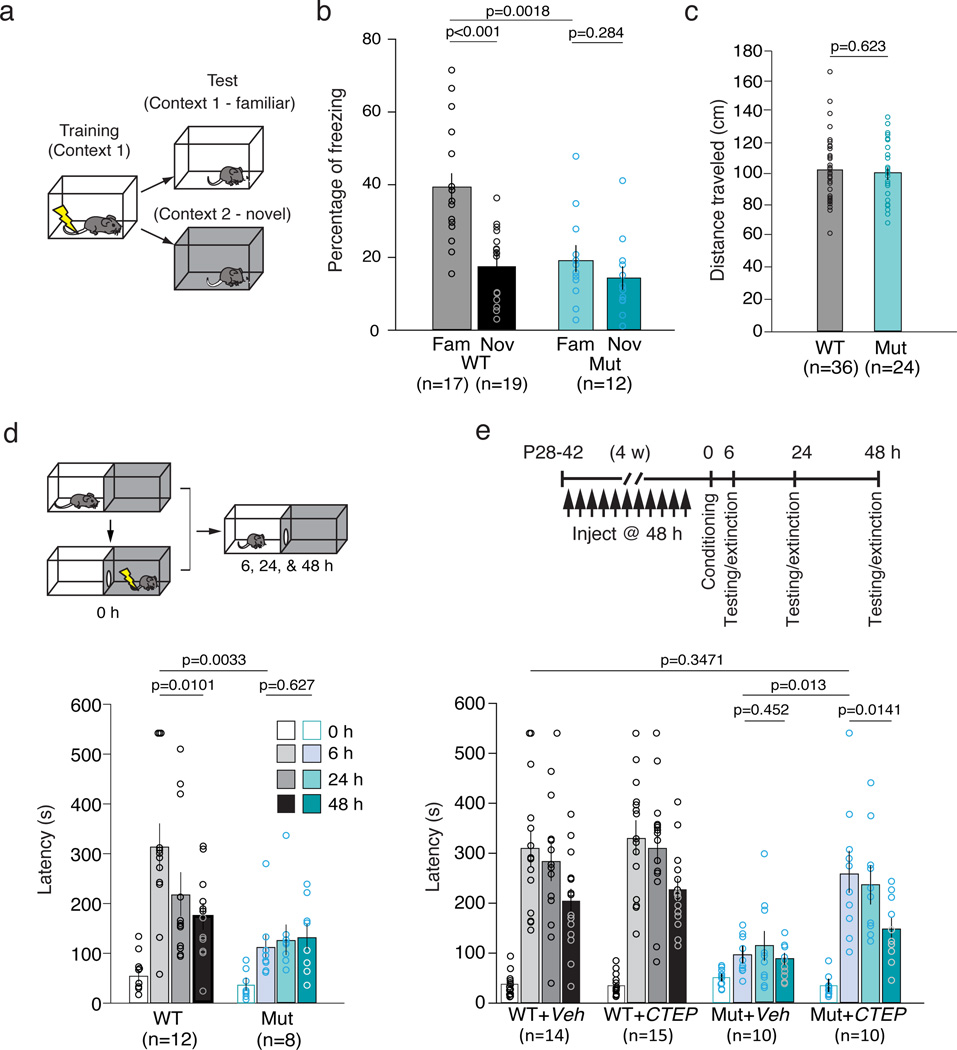
Figure 2. 16p11.2 df/+ mice exhibit deficits in hippocampal-associated contextual fear conditioning (CFC) and inhibitory avoidance (IA).
(a) CFC experimental design. (b) Mutant mice show significantly less freezing in the familiar context compared with WT (unpaired t-test, p = 0.0018). While WT mice are able to distinguish a novel from familiar context (unpaired t-test, p < 0.0001), the mutant mice are impaired (unpaired t-test, p = 0.2840). Two-way ANOVA, genotype × context, p = 0.0166. (c) Mutant and WT mice have the same running response to foot-shock during the training session (unpaired t-test, p = 0.6234). (d) Mutant mice are impaired in IA acquisition (WT vs Mut, 0 hr vs 6 hr, repeated measures two-way ANOVA, p = 0.0108; WT vs Mut at 6 hr, post-hoc unpaired t-test, p = 0.0033). Unlike WT (6 hr vs 48 hr, post-hoc paired t-test, p = 0.0101), mutant mice show no extinction of fear memory (WT vs Mut, 6 hr vs 48 hr, repeated measures two-way ANOVA, p = 0.0197; Mut, 6 hr vs 48 hr, post-hoc paired t-test, p = 0.6278). (e) CTEP treatment ameliorates behavioral deficits in mutant mice in IA. In mutant mice, CTEP treatment enhances acquisition (Mut+Veh vs Mut+CTEP, 0 hr vs 6 hr, repeated measures two-way ANOVA, p = 0.0016; Mut+Veh vs Mut+CTEP at 6 hr, post-hoc unpaired t-test, p = 0.0013) and extinction of fear memory (Mut+Veh vs Mut+CTEP, 6 hr vs 48 hr, repeated measures two-way ANOVA, p = 0.0039; Mut+Veh, 6 hr vs 48 hr, post-hoc paired t-test, p = 0.4281; Mut+CTEP, 6 hr vs 48 hr, post-hoc paired t-test, p = 0.0140). There is no statistically significant difference between WT+Veh and Mut+CTEP at 6 hr (unpaired t-test, p = 0.3471). In WT mice, CTEP has no effect on either acquisition (WT+Veh vs WT+CTEP, 0 hr vs 6 hr, repeated measures two-way ANOVA, p = 0.6564) or extinction of fear memory (WT+Veh vs WT+CTEP, 6 hr vs 48 hr, repeated measures two-way ANOVA, p = 0.9882). All data are plotted as mean ± SEM with individual values superimposed.