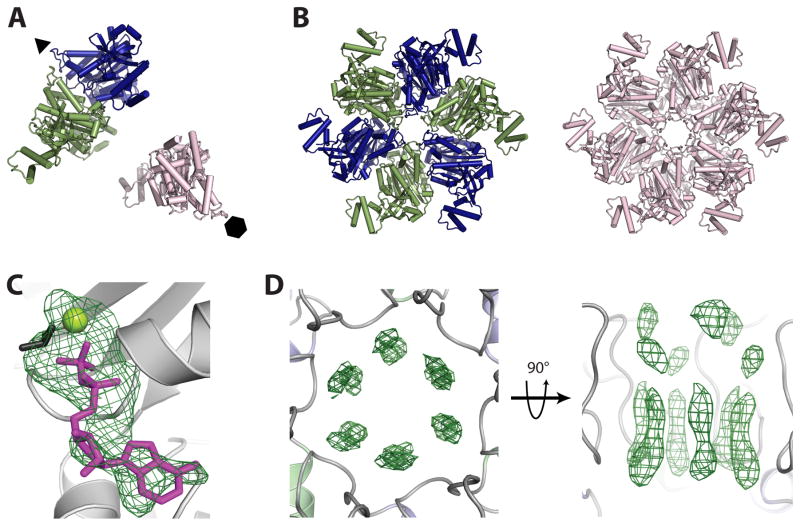
Figure 2. Structure solution and ligand binding in crystal-form II.
A) Molecular replacement reveals one Rho dimer (blue/dark grey and green/grey) and one monomer (pink/light grey) per asymmetric unit. Crystallographic six- and three-fold symmetry axes are indicated by a hexagon and triangle, respectively.
B) Crystallographic symmetry generates one three-fold symmetric trimer-of-dimers (blue/dark grey and green/grey) and one six-fold symmetric hexamer (pink/light grey). These structures represented our first crystallographic views of a full-length, closed-ring Rho hexamer.
C) Initial refinement of molecular replacement solutions produced Fo−Fc difference electron density maps revealing the presence of nucleotide (modeled as ADP•BeF3) at all three ATP binding sites per asymmetric unit. ADP is colored magenta/grey, BeF3 is colored black, and the Mg2+ ion is colored yellow-green/light grey. Electron density (green mesh) is contoured at 3σ.
D) Initial refinement of molecular replacement solutions produced Fo−Fc difference electron density maps revealing the presence of RNA in the central channel of each Rho hexamer. The RNA density appeared to be averaged around the crystallographic symmetry axis, producing un-interpretable maps. Electron density (green mesh) is contoured at 2.5σ.