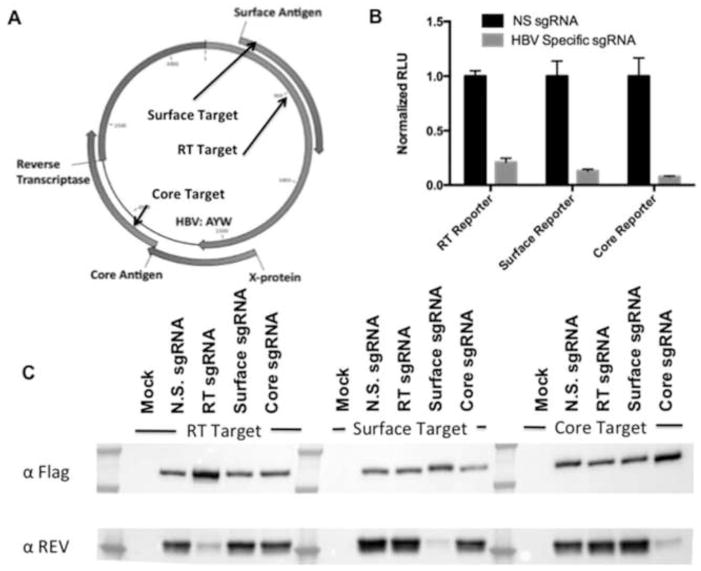
Figure 1. HBV targeting strategy and sgRNA optimization.
To target HBV DNA intermediates in infected cells, we designed sgRNAs specific for the HBV surface Ag, core, and RT ORFs, as depicted in panel A. To assess efficacy, fusion protein-based indicator plasmids, which encode an amino-terminal HIV-1 Rev-derived epitope tag, an in-frame HBV-derived target, and a carboxy-terminal FLuc indicator gene, were employed. As shown in panel B, all three sgRNA candidates effectively inhibited FLuc expression from their cognate reporter plasmid in co-transfected 293T cells when compared to a control, non-specific (N.S.) sgRNA. In panel C, expression of the same fusion protein was probed by Western blot using a previously described α-Rev rabbit polyclonal antiserum (Kennedy et al., 2014). Co-expression of Cas9 was confirmed using an antibody specific for the FLAG epitope tag present on this protein. When the reporter was cognate for the sgRNA, a marked reduction of the expression level of the fusion protein target could be observed, confirming the specificity and efficacy of each sgRNA tested.