Figure 8. Immunolabeling analysis for microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2), neuronal density and astrogliosis in the frontal cortex of APPtg mice treated with bithionol, mitoxantrone and hexachlorophene.
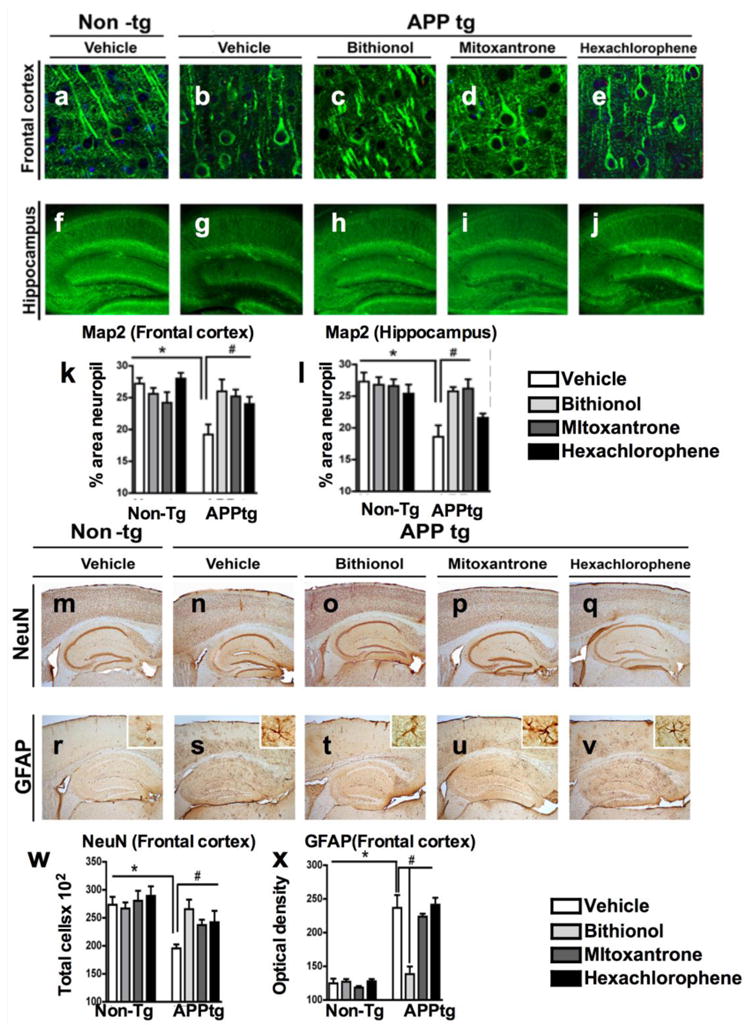
Vibratome sections of the frontal cortex (a-e) and the hippocampus (f-j) were immunolabeled with anti-MAP2 antibody, a neuronal-specific protein localized to the cytoskeleton, and the nuclei were stained by DAPI. The sections were visualized with the laser scanning confocal microscope (k-l). Computer-aided quantitative analysis of the area of neuropils (%) covered by MAP2 immunoreactivity. The effect of the compounds was also examined for neuronal density and astrogliosis using an antibody against the neuronal marker NeuN (m-q), and against the astrocytic marker GFAP (r-v). In the graphs (w-x), the analysis of the frontal cortex NeuN immunoreactivity and GFAP immunoreactivity across the experimental groups. *p<0.05 compared with APPtg
