Figure 11.
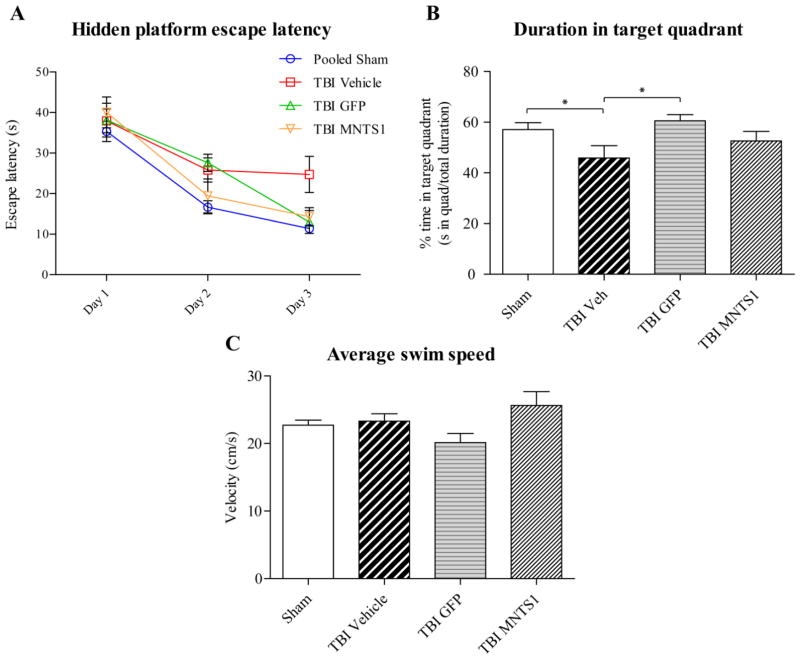
Cell transplantation improved hippocampal-dependent cognitive outcomes. Five weeks post surgery, all groups underwent the MWM hidden platform task. A) After 3 days of testing, post-hoc analysis revealed that both NPC-transplanted TBI groups and sham animals had significantly reduced escape latencies on the hidden platform task relative to TBI/vehicle controls (TBI/vehicle vs. sham: ##p < 0.001; TBI/vehicle vs. TBI/GFP, *p = 0.031; TBI/vehicle vs. TBI/MNTS1: +p = 0.025). Two-way repeated measures ANOVA was significant for trial day (p < 0.001), group (p = 0.005), but not for trial day × group interaction (p = 0.088). B) On Day 3, sham and TBI/GFP groups spent a greater percentage of time in the target quadrant compared to vehicle control animals. C) There were no significant differences in swim speeds among groups suggesting that the injury did not affect swimming skills.