Figure 4.
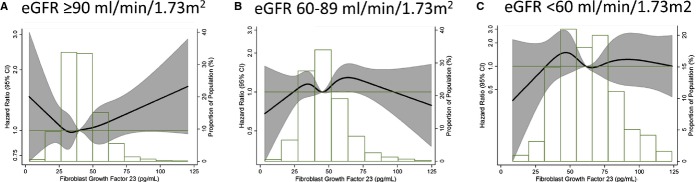
Association of circulating FGF‐23 concentrations with incidence of atrial fibrillation presented as hazard ratio (HR; solid line) and 95% confidence intervals (CI; shaded area) by categories of eGFR (<60 (panel C), 60 to 89 (panel B), and 90+ mL/min per 1.73 m2 (panel A)). Results from Cox proportional hazards model with FGF‐23 modeled using restricted cubic splines, adjusted for age, sex, race, study site, body mass index, smoking, education, height, diabetes, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, use of antihypertensive medication, prevalent coronary heart disease, prevalent heart failure, ECG‐based left ventricular hypertrophy, NT‐proBNP, high‐sensitivity C‐reactive protein, and eGFR. Median value of FGF‐23 was considered the reference (HR=1). The histograms represent the frequency distribution of FGF‐23 in each category of eGFR. Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study, 1990–2010. eGFR indicates estimated glomerular filtration rate; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; NT‐proBNP, N‐terminal prohormone of brain natriuretic peptide.
