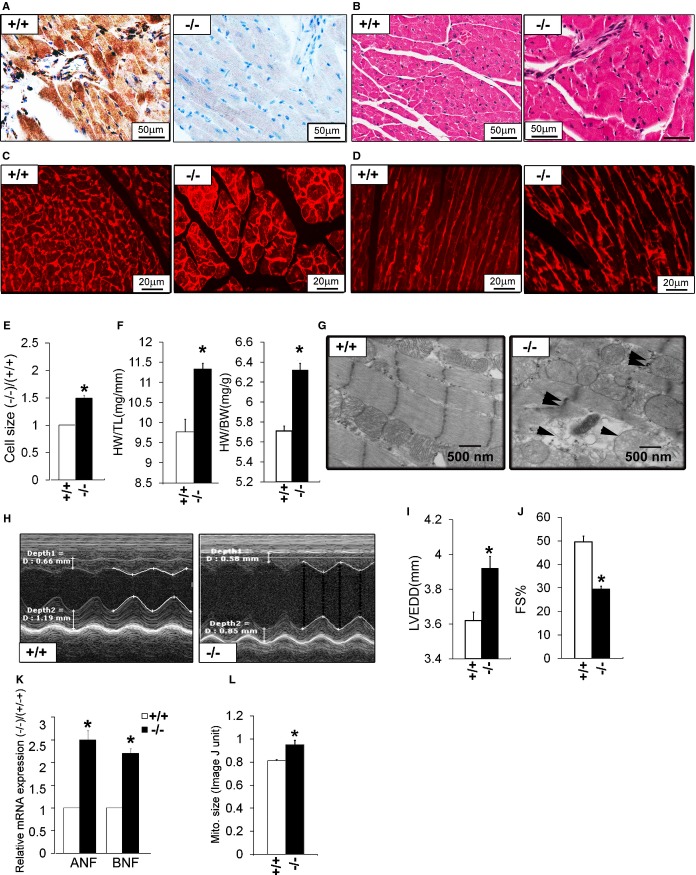
Figure 3.
Cardiac phenotype in adult ERp44−/− mice. A, Immunohistochemistry for ERp44 in hearts of ERp44+/+ and ERp44−/− mice and (B) H&E‐stained heart sections. C and D, Wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) staining in ERp44+/+ and ERp44−/− hearts. E, Quantification of cell size using ImageJ (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD) analysis of WGA‐stained hearts (n=150/genotype; P<0.05). F, Heart mass to tibia length (HW/TL) and body weight (HW/BW) (n=5/genotype; *P<0.05). G, EM analysis reveals swelling, structural disruption, and membrane rupture in the mitochondria (arrows) in late‐stage ERp44−/− mice. H, Cardiac function assessed in mice using M‐mode echocardiography. I, LV internal diameters in diastole (LVIDd) and (J) fractional shortening (FS) measurements. K, Expression of ANF and BNF in hearts were quantified by qRT‐PCR (n=3/genotype; *P<0.05). (L) Quantification of mitochondrial size using ImageJ analysis of EM heart images. Mean values±SEM were determined (n=5/genotype; *P<0.05). ANF indicates atrial natriuretic factor; BNF, B‐type natriuretic factor; EM, electron microscopy; ERp44, endoplasmic reticulum resident protein 44; LV, left ventricle; LVEDD, LV end‐diastolic diameter; qRT‐PCR, quantitative real‐time polymerase chain reaction.