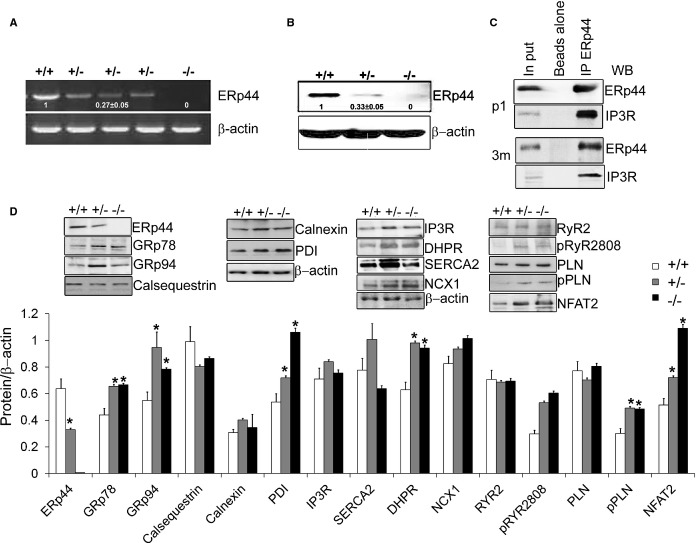
Figure 5.
Immunoblot analysis of ERp44‐deficient MNCs. A and B, qRT‐PCR and immunoblot analysis of ERp44 expression in ERp44+/+, ERp44+/−, and ERp44−/− MNCs (n=6/genotype). C, P1 and 3‐month cardiomyocytes were isolated and treated with 2 mmol/L of DPS in Krebs‐Ringer phosphate buffer (KRPB) for 30 minutes and washed 3 times with KRPB and subjected to IP with anti‐ERp44 and control set of beads using rabbit IgG with beads alone, and samples analyzed by immunoblot with the anti‐IP3R, and anti‐ERp44 antibodies. Input controls were included. D, Immunoblot analysis of ER proteins, Ca2+ channels handling proteins and p‐RyR S2808, p‐PLN (Ser16/Thr17) in the ERp44+/+, +/−, and −/− mouse neonatal P1 heart tissues. Nuclear NFAT2 levels were assessed using enriched nuclear proteins (n=3/genotype; *P<0.05). Experiments were repeated 3 times independently. DHPR indicates dihydropyridine receptor; DSP, dithiobis[succinimidyl propionate]; ERp44, endoplasmic reticulum resident protein 44; IP, immunoprecipitation; IP3R, inositol trisphosphate receptor; MNCs, mouse neonatal cardiomyocytes; NCX, sodium‐calcium exchanger; NFAT2, nuclear factor of activated T‐cell transcription factor 2; PDI, protein disulfide isomerase; PLN, phospholamban; qRT‐PCR, quantitative real‐time polymerase chain reaction; RyR, ryanodine receptor; SERCA2a, sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase; WB, Western blot.