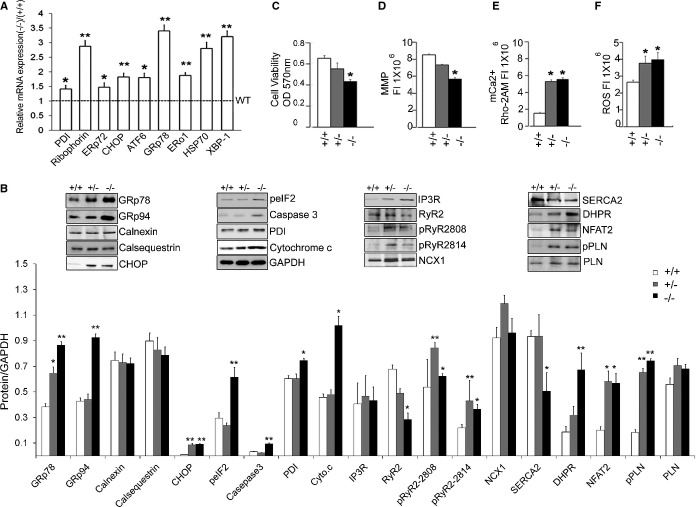
Figure 7.
Activation of cellular responses in the ERp44‐deficient models. A, qRT‐PCR detecting expression of ER stress genes in adult hearts of ERp44−/− and ERp44+/+ mice (n=3/genotype). B, Immunoblot analysis of ER proteins, Ca2+ handling proteins, apoptosis markers, cytochrome c, and nuclear NFAT2 in heart from ERp44+/+, +/−, and −/− mice (n=3/genotype). C, MTT viability assay (n=6/genotype). D, MMP assay (n=6/genotype) and (E) mkitochondrial Ca2+ levels (Rhod‐2AM) were detected in MNCs (n=6/genotype). F, ROS were assessed after treatment with Tu (5 μg/mL) for 24 hours using the ROS assay kit (n=6/genotype; *P<0.05; **P<0.01). Experiments were repeated 3 times independently. ATF indicates activating transcription factor; CHOP, CCAAT‐enhancer‐binding protein homology protein; DHPR, dihydropyridine receptor; ERo, endoplasmic reticulum membrane oxidoreductase; ERp44, endoplasmic reticulum resident protein 44; GRp, glucose‐regulated protein; HSP, heat shock protein; IP3R, inositol trisphosphate receptor; MMP, mitochondrial membrane potential; MNCs, mouse neonatal cardiomyocytes; MTT, 3‐(4,5‐dimethylthiazol‐2‐yl)‐2,5‐diphenyltetrazolium bromide; NCX, sodium‐calcium exchanger; NFAT2, nuclear factor of activated T‐cell transcription factor 2; PDI, protein disulfide isomerase; PLN, phospholamban; qRT‐PCR, quantitative real‐time polymerase chain reaction; ROS, reactive oxygen species; RyR, ryanodine receptor; SERCA2a, sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase; XBP, X‐box protein.