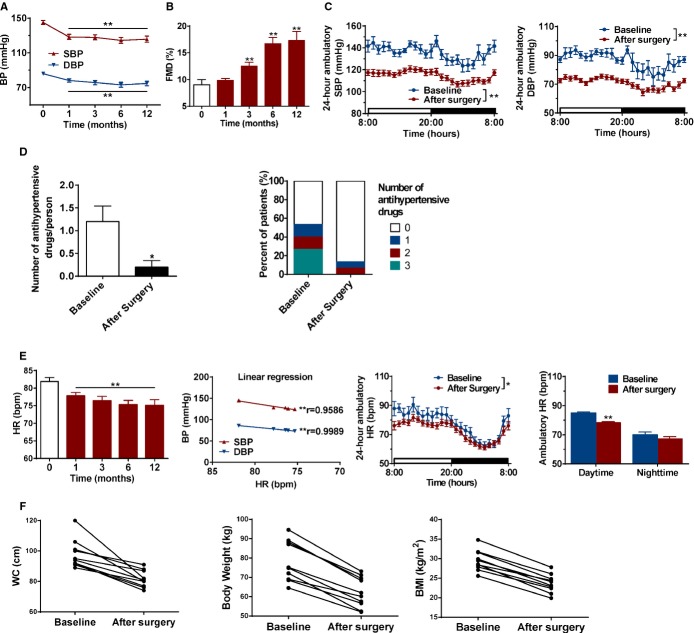
Figure 7.
Effect of metabolic surgery on blood pressure (BP) in hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes. A, Time courses of systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) in hypertensive patients. BP was measured by mercury sphygmomanometer. **P<0.01 vs. baseline. Data are means±SEM. Each n=9 to 21. B, Flow‐mediated dilation (FMD) in hypertensive patients who underwent metabolic surgery was measured at 0 (baseline), 1, 3, 6, and 12 months. **P<0.01 vs. baseline. Data are means±SEM. Each n=9 to 21. C, The 24‐hour ambulatory SBP and DBP was monitored from hypertensive patients at baseline or 6 months after metabolic surgery. **P<0.01 vs. baseline. Data are means±SEM. Each n=17 to 21. D, Usage of antihypertensive drugs from hypertensive patients at baseline or after metabolic surgery. *P<0.05 vs. baseline. Data are means±SEM. Baseline (n=21) and after surgery (n=17). E, The time courses of RYGB reduced HR from hypertensive patients and a linear correlation between HR and BP. The 24‐hour ambulatory HR change after surgery, daytime, and nighttime HR were measured at month 6. *P<0.05; **P<0.01 vs. baseline. Data are means±SEM. Each n=9 to 21. F, Scatter plot graphic for WC, body weight, and BMI of hypertensive patients at baseline or 12 months after metabolic surgery. Baseline and after surgery (n=10). BMI indicates body mass index; HR, heart rate; RYGB, Roux‐en‐Y gastric bypass; WC, waist circumference.