Figure 1.
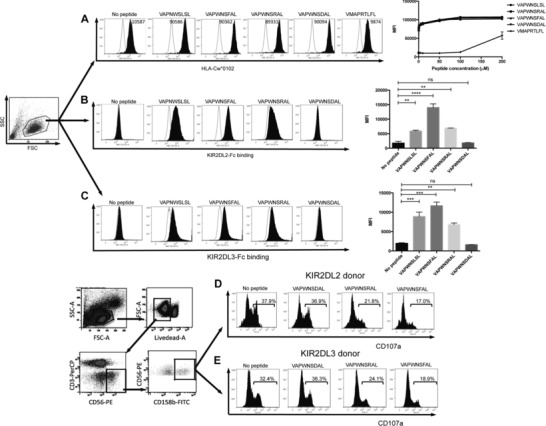
Correlation of KIR binding with NK cell inhibition in KIR2DL2+ and KIR2DL3+ donors. (A) Stabilization of HLA‐Cw*0102 on 721.174 by the indicated VAPWNSLSL derivative peptides and a control peptide (VMAPRTLFL) at saturating concentrations 10 μM (filled histograms). The no primary Ab control is indicated in each plot and the titration of the peptides is shown in the far right panel. Binding of (B) KIR2DL2 or (C) KIR2DL3 fusion constructs to 721.174 cells in the presence (filled lines) or absence of the indicated peptide at a concentration of 10 μM. Representative histograms (n = 3 samples) are shown. Summaries of the mean fluorescence intensities (MFI) of KIR‐binding pooled from two independent experiments are shown in the far right panels (**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; Student's t‐test). Gating strategy and degranulation assays of CD158b‐positive CD3‐CD56+ NK cells from (D) KIR2DL2 homozygous or (E) KIR2DL3 homozygous donors in response to 721.174 cells incubated with the indicated peptides at a final concentration of 10 μM. Representative histograms of six 2DL2 and eight 2DL3 donors, analyzed in duplicate, are shown.
