Figure 3.
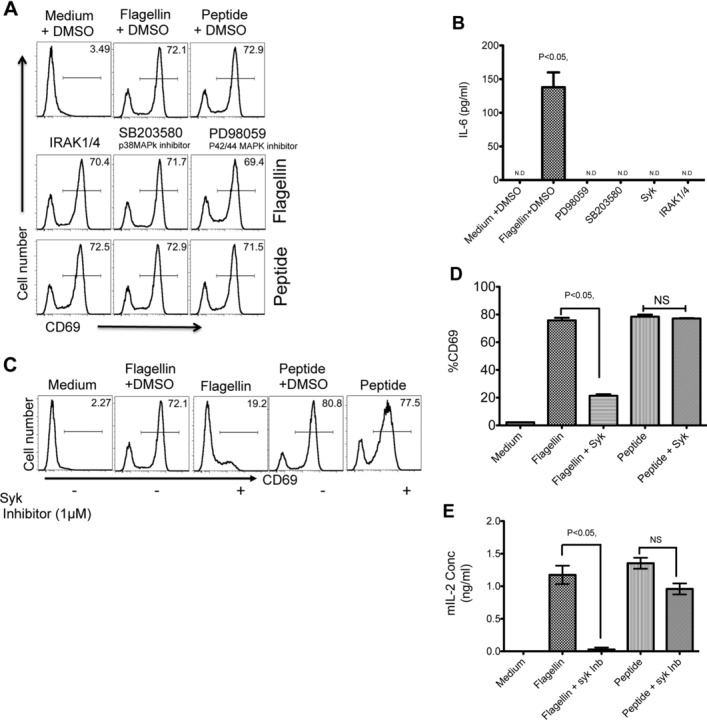
Syk is required for optimal activation of DCs and flagellin-specific T cells. (A) The role of IRAK1/4, p38, and p42/44 MAPK was examined by inhibition with 50 μM of specific pharmacological inhibitors IRAK1/4 inhibitor, p38 MAPK inhibitor (SB203580), and p42/44 MAPK inhibitor (PD98059). In total, 1 × 105 CD11c+ DCs were treated with inhibitors or left untreated for 30 min before incubation with 1 × 105 SM1 T cells, 10 ng/mL of flagellin, or 6 μM of flagellin peptide (427–441). SM1 (CD4+CD90.1+) T-cell activation was determined as CD69 expression by flow cytometry 16 h after flagellin stimulation. (B) IL-6 production was assayed in culture supernatants of DCs treated with various pharmacological inhibitors as mentioned above and cultured with SM1 T cells in a 1:1 ratio for 16 h by ELISA. (C) CD11c+ DCs were pretreated with 1 μM of Syk inhibitor (Bay IV 61–016) or DMSO before incubating with 1 × 105 SM1 T cells flagellin or peptide stimulation. Representative flow cytometry plots (n = 3 samples per group) show CD69 expression on (CD4+CD90.1+) SM1 T cells 16 h after flagellin or peptide stimulation, as measured by flow cytometry. (D) The percentage of CD69 expression as measured in (C). (E) Production of IL-2 in culture supernatants was assessed by ELISA 16 h after incubation with medium, flagellin, peptide, in the presence or absence of Syk inhibitor. (B, D, and E) Data are shown as mean ± SEM of three samples per group, and are from one single experiment representative of two independent experiments. NS: nonsignificant by unpaired t-test.
